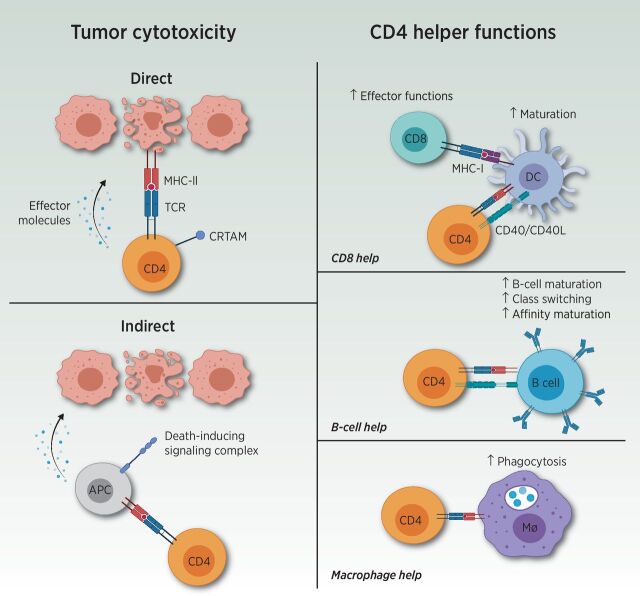
Figure 1.
Overview of CD4 T-cell functions. CD4 T cells are most well known for their Th cell functions (displayed on the right). Through recognition of the TCR of the peptide-MHC complex, CD4 T cells mediate increased maturation and activation of DCs. This process allows augmented CD8 T-cell effectors upon interaction with the activated DCs. Furthermore, CD4 T cells increase B-cell maturation, antibody class switching, and affinity maturation, and enhance phagocytosis within macrophages (Mφ). Aside from helper functions, CD4 T cells possess both direct and indirect tumor cytotoxicity capacities (displayed on the left). Direct cytotoxicity was demonstrated by cytotoxic CD4 T expressing class I–restricted T-cell–associated molecule (CRTAM). Indirect cytotoxicity could also be guided by CD4 T cells through interaction with antigen-presenting cells (APC) or natural killer cells. Adapted from an image created with BioRender.com.