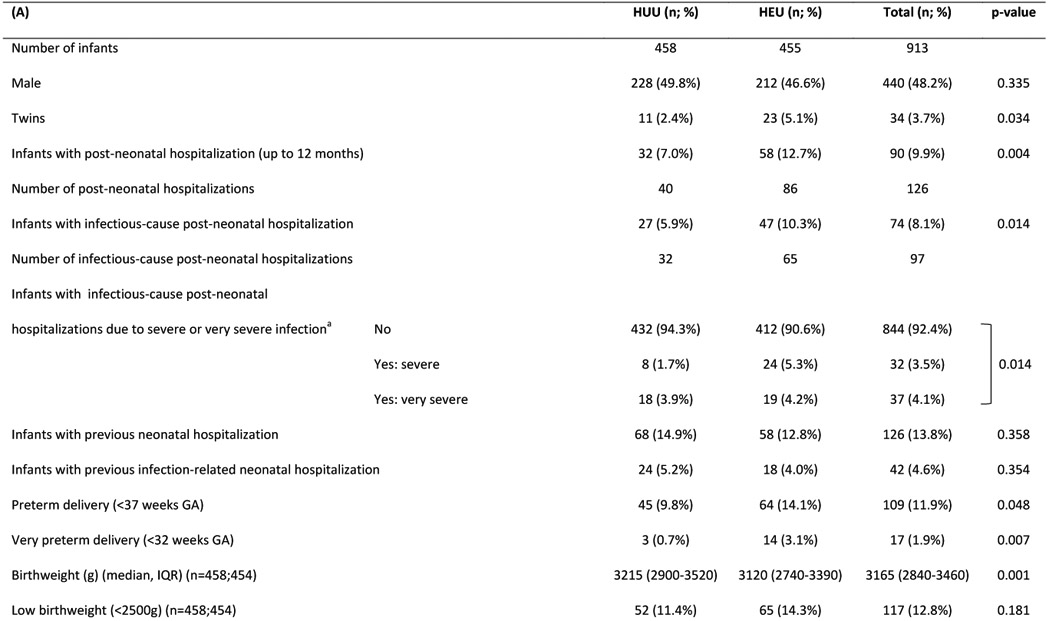
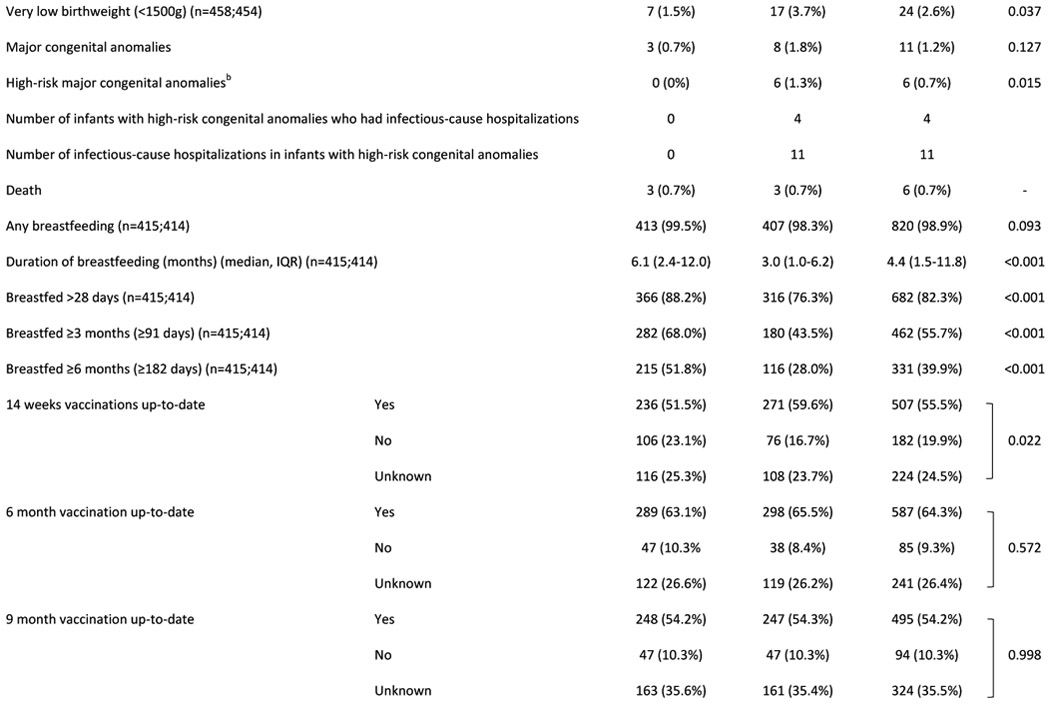
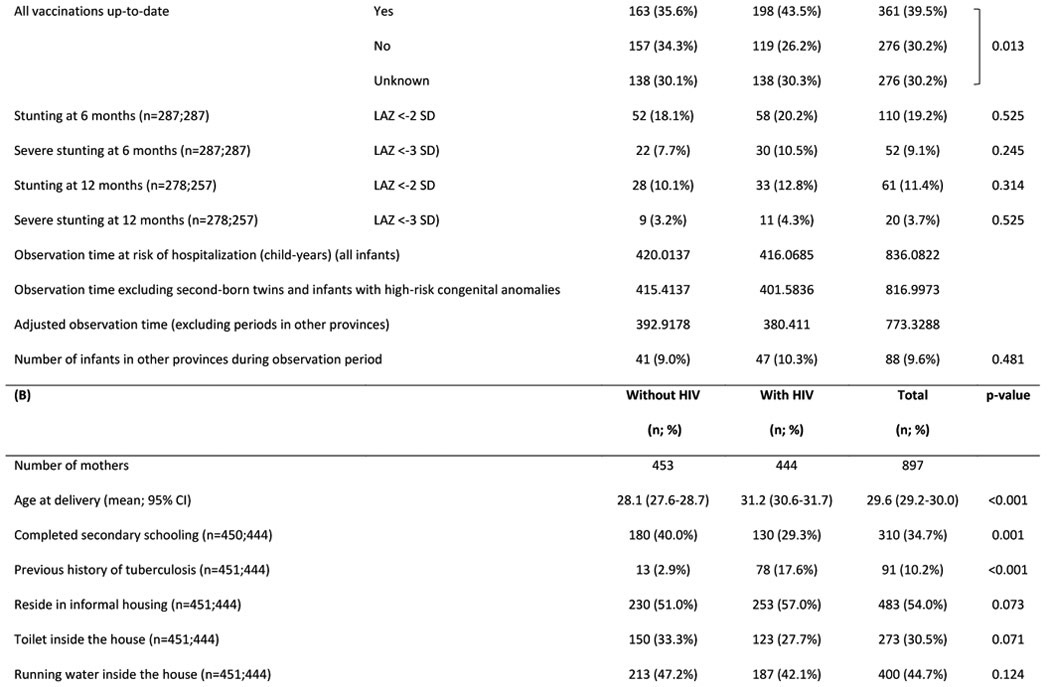
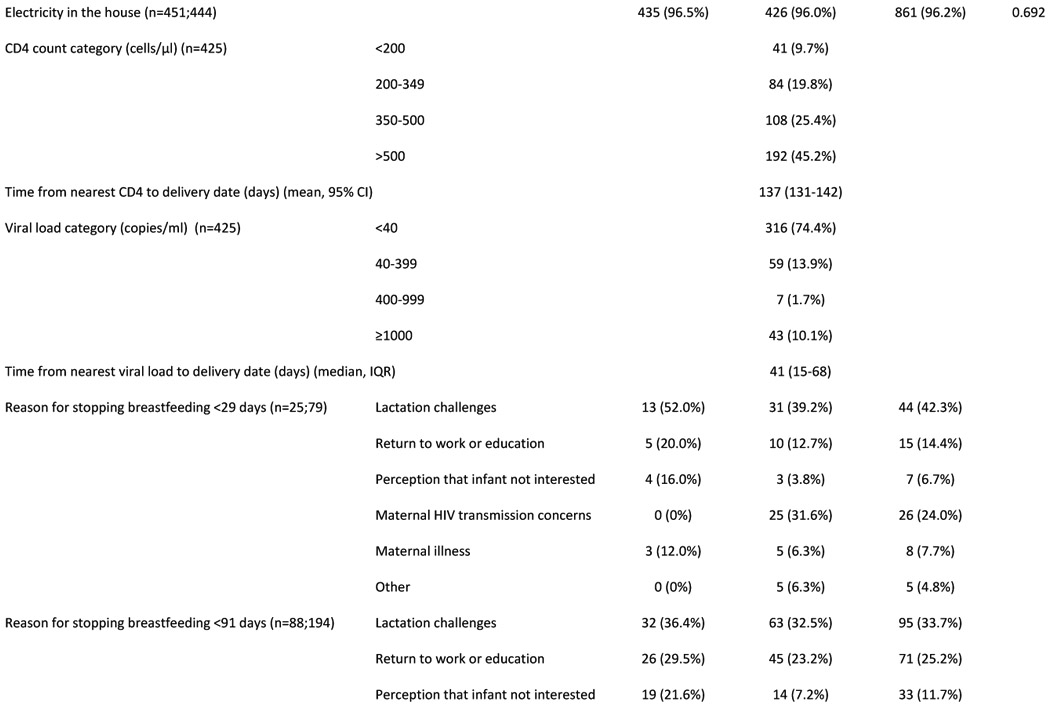
Table 1:
Characteristics of (A) HIV uninfected infants and (B) their mothers
|
|
|
|

|
Abbreviations: HUU – HIV-unexposed uninfected; HEU – HIV-exposed uninfected; GA - gestational age; g - grams; IQR - interquartile range; LAZ - length-for-age Z-score; SD – standard deviation; CI - confidence interval; ART - antiretroviral treatment
Graded with Pediatric Infectious Event Tool for Research; most severe infection grade during any hospitalization was selected
Major congenital anomalies regarded as high-risk for infection-related hospitalization: myelomeningocele (x2); VACTERL syndrome; cleft palate; laryngeal cleft; Trisomy 21 with cardiac defect. (Note: the following major congenital anomalies were not regarded as high-risk: talipes equinovarus (x2); Klinefelter syndrome; polydactyly; thoracic scoliosis.)
