Figure 3.
High-resolution profiling of antibody footprints reveals conserved public peanut epitopes
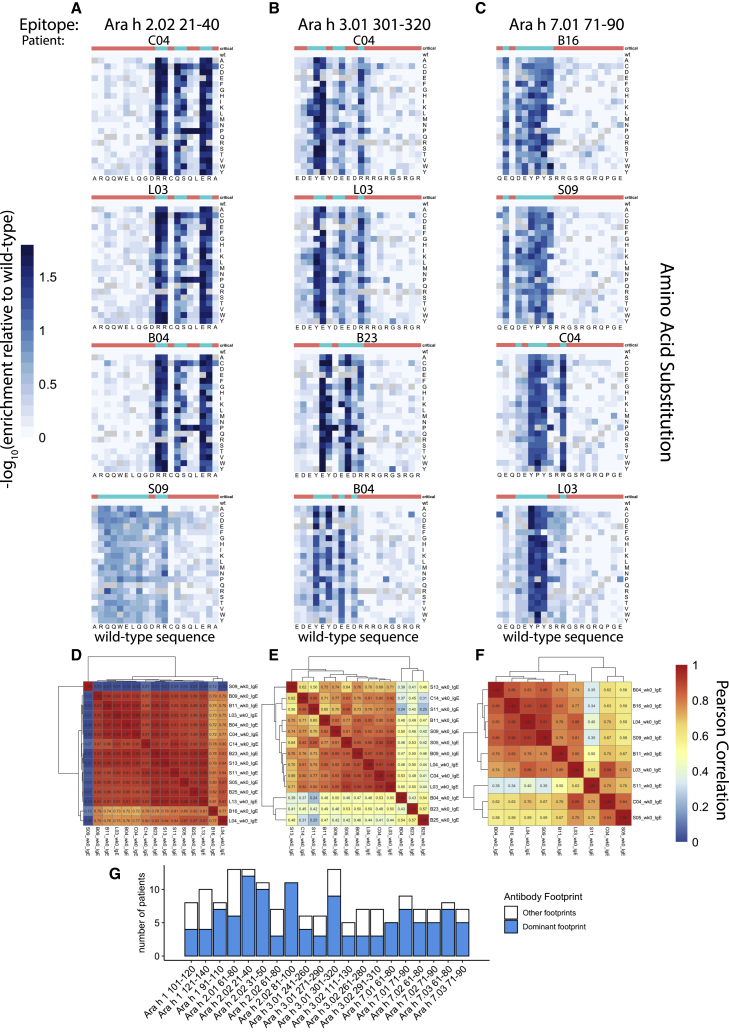
(A–C) Representative examples of high-resolution antibody footprints from allergic patients (week 0 samples) for public peanut epitopes Ara h 2.02 aa21–40 (A), Ara h 3.01 aa301–320 (B), and Ara h 7.01 aa71–90 (C). Heatmaps plot the −log10 transformed relative enrichment compared to the adjusted wild-type value, which represents the substitution effects on antibody binding. x axis, amino acid sequence of the wild-type peanut epitope; y axis, amino acid substitutions. Critical residues for antibody binding are indicated at the top of each heatmap in blue; non-critical residues are indicated in red.
(D–F) Pairwise Pearson correlations between high-resolution footprints of all allergic patients with antibody responses to the three peptides from (A)–(C), respectively.
(G) Number of patients who share the dominant IgE antibody footprint for the public epitopes indicated by the x axis. Blue, patients who share the dominant footprint; white, patients with non-dominant footprints.