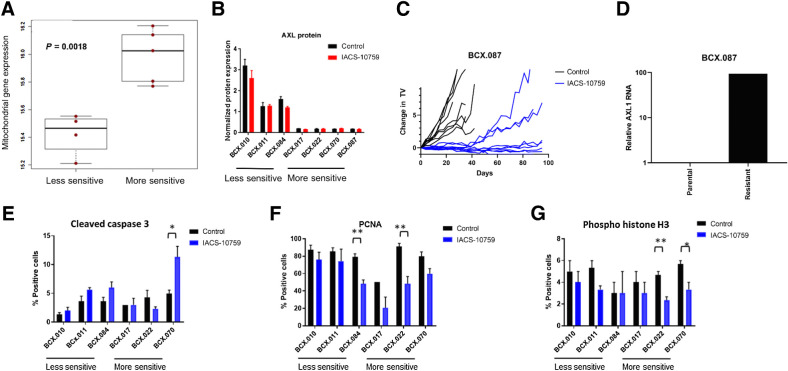
Figure 3.
Predictor of response to IACS-10759 in TNBC. A, Using baseline RNA-seq analysis for PDX with known IACS-10759 sensitivity, we found that protein-coding mitochondrial genes are expressed significantly higher in PDXs more sensitive to IACS-10759. B, AXL protein as determined by RPPA is higher in PDXs less sensitive to IACS-10759. C and D, A highly sensitive PDX was treated for >90 days (individual tumors shown) and sporadic tumors began growing, and a reformed tumor had increased AXL1 mRNA expression compared with the control. E–G, We treated a select set of PDXs with ranges of responses to IACS-10759 (5 mg/kg, orally, 5 days on 2 days off) and collected the tumors after 12 days of treatment. We analyzed the samples for CC3 (E), PCNA (F), and phosphohistone H3 (G). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.