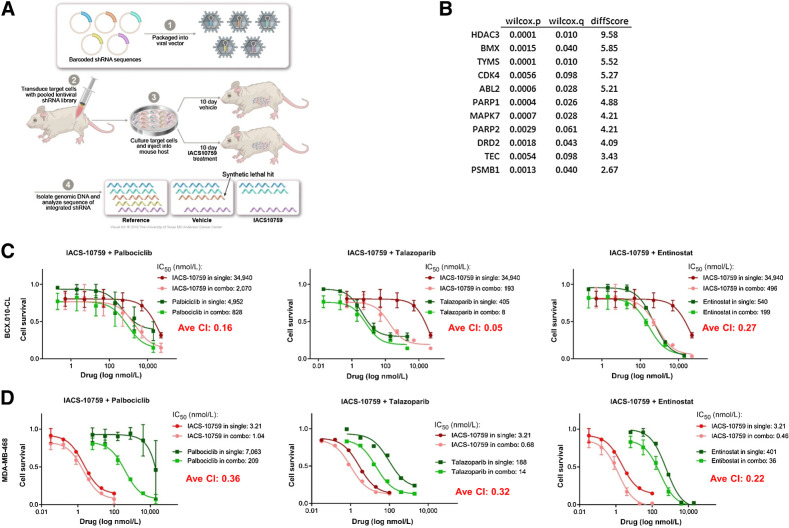
Figure 5.
Identification of combination partners for IACS-10759 using in vivo synthetic lethality screen. A, Illustration of method used to identify genes (from gene panel linked to FDA-approved agents) whose suppression led to increased cell loss in presence of IACS-10759 in mice. B, List of genes identified in screen. We chose to validate CDK4, PARP1, and HDAC3 using palbociclib, talazoparib, and entinostat, respectively. C and D, IACS-10759 was synergistic (CI < 1) with palbociclib, talazaparib, and entinostat in BCX.010-CL and MDA-MB-468 cells as assessed by cell growth assays. Ave CI, average combination index.