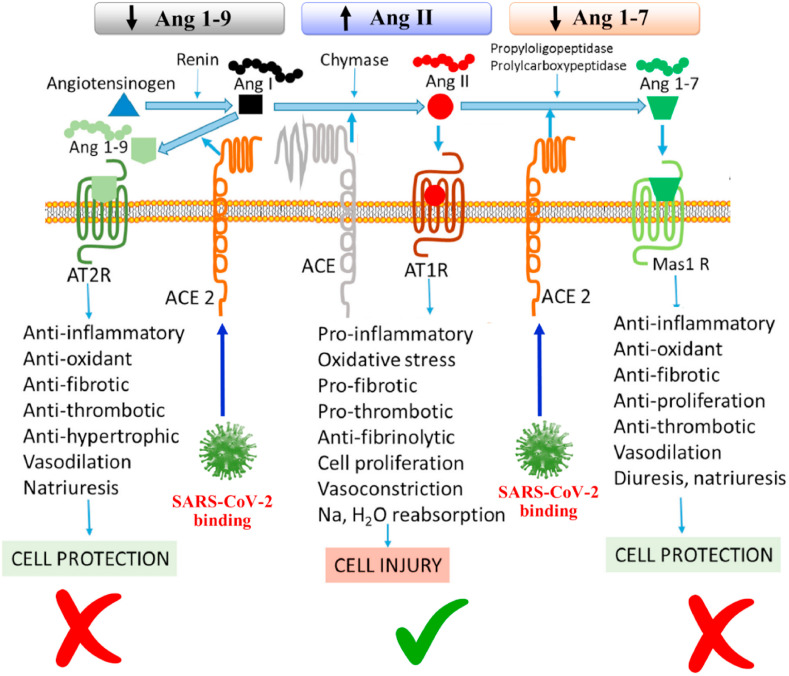
Fig. 3.
Links between SARS-CoV-2 infection and highly abundant Angiotensin II leading to various pathogenic downstream effects. Binding of SARS-CoV-2 to the ACE2 receptor on the cell surface decreases ACE2 abundance and increases the level of Angiotensin II whilst reducing Ang 1–9 and Ang 1–7. This can lead to inflammation, oxidative stress, fibrosis, thrombosis, cell proliferation, salt and water retention and vasoconstriction, hence inducing cell injury. Adapted from Ref. [167] with the permission of Elsevier.