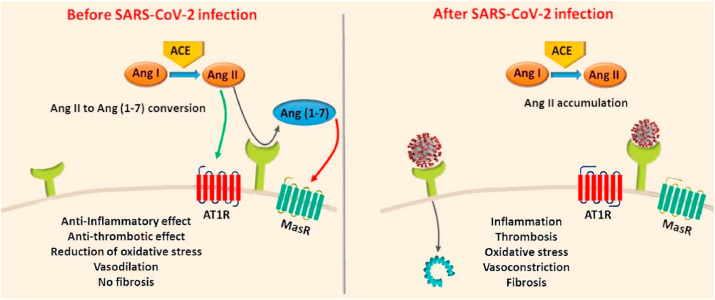
Fig. 4.
In healthy individuals, Angiotensin II is converted into Angiotensin (1–7) via ACE2. However, in COVID19, ACE2 may be dysfunctional due to the binding of SARS-CoV-2, which can affect the conversion of Angiotensin II to Angiotensin (1–7). This results in the accumulation of Angiotensin II in the infected person and induces proinflammatory, prothrombotic, fibrotic and vasoconstrictive downstream effects. In the presence of CVD, however, the RAAS could be impaired. Consequently, upon infection with SARS-CoV-2, more Angiotensin II could accumulate resulting in serious cardiovascular complications.