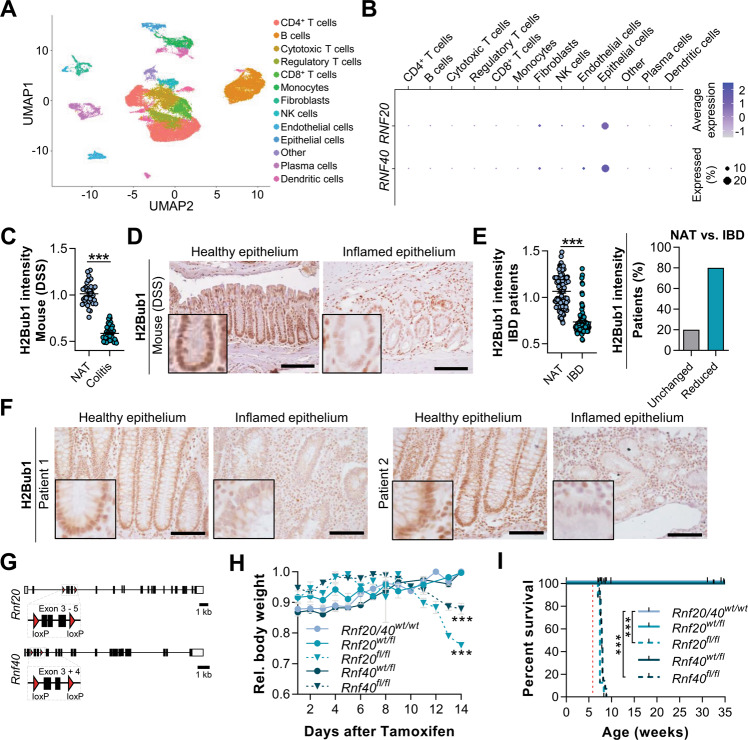
Fig. 1. IBD patients display H2Bub1 loss in inflamed intestinal epithelium.
A Cell type clustering in a uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) based on scRNA-seq data evaluating cell-specific gene expression changes between uninflamed and inflamed resection specimens isolated from Crohn’s disease patients [20]. B Dot plot displaying the expression level and the percentage of cells within each cell cluster expressing RNF20 and RNF40. RNF20 and RNF40 levels were highest in epithelial cells. C Colon sections of C57BL/6N mice treated with 0.75% DSS (n = 6) for 14 days were stained for H2Bub1 using IHC. Relative staining intensity was quantified using FIJI in five images per mouse. D Representative images of murine colon sections displaying reduced H2Bub1 levels in inflamed epithelium. Scale bar: 100 µm. E Intestinal sections of Crohn’s disease patients (n = 18) were stained for H2Bub1 using IHC. Relative staining intensity was quantified using FIJI in five images per patient. When comparing healthy resection margins to inflamed tissue, 80% of patients displayed reduced H2Bub1 levels in inflamed regions. F Representative images of colon sections of two IBD patients stained for H2Bub1. Scale bar: 100 µm. G Mice with loxP-flanked exons 3–5 of Rnf20 or loxP-flanked exons 3–4 of Rnf40 were mated with Villin-CreERT2 mice to enable a tamoxifen-inducible intestinal knockout of Rnf20 or Rnf40, respectively. H Fourteen days after the first tamoxifen injection, Rnf20fl/fl and Rnf40fl/fl mice displayed severe weight loss and, therefore, (I) significantly reduced survival (red dotted line represents start of tamoxifen treatment). Survival data were based on local and institutional guidelines according to which animals needed to be sacrificed after a weight loss of 20%. One-way ANOVA, mean ± SEM.