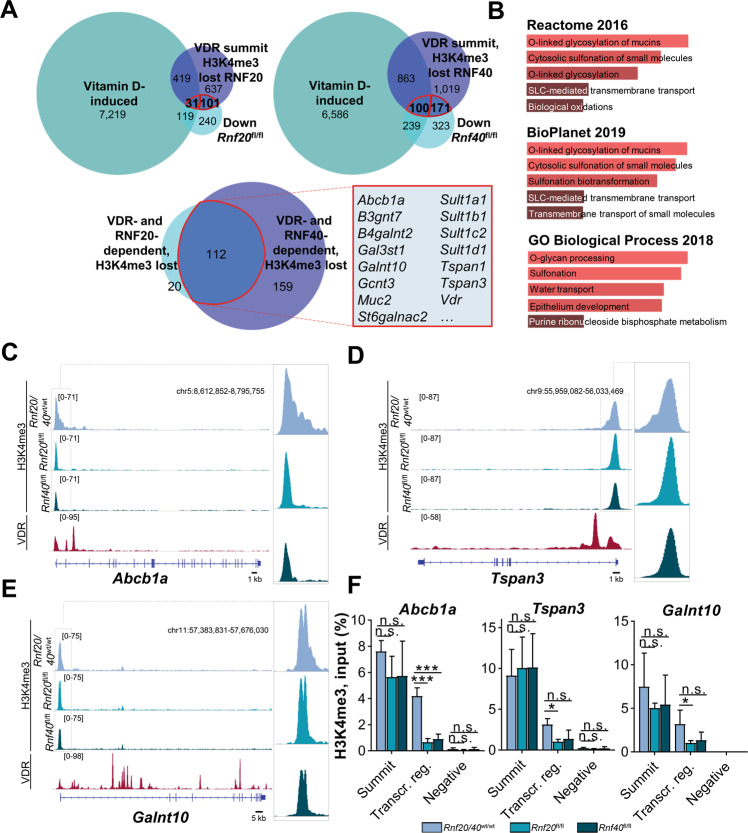
Fig. 5. RNF20 and RNF40 are required for transcriptional elongation-associated H3K4me3 spreading on VDR target genes.
A Venn diagram displaying the overlap between vitamin D-induced genes [29], genes downregulated following Rnf20 or Rnf40 knockout in IECs identified by mRNA-seq and VDR-dependent genes displaying reduced H3K4me3 occupancy upon Rnf20 or Rnf40 deletion in IECs (upper panel). Numbers marked in red were overlapped to identify VDR- and RNF20/40-dependent genes with reduced H3K4me3 occupancy (lower panel). B Enrichr gene ontology analysis of these 112 genes revealed their involvement in O-linked glycosylation and sulfonation of proteins. C–E ChIP-seq tracks of three exemplary genes (Abcb1a, Tspan3, Galnt10) illustrated H3K4me3 peak narrowing in Rnf20 and Rnf40 knockout IECs and VDR occupancy in murine small intestine [29]. F ChIP-qPCR for Abcb1a, Tspan3 and Galnt10 was performed using primers complementary to the peak summit, in the transcribed region and a negative control site. Upon Rnf20 and Rnf40 deletion, occupancy in the transcribed region was significantly decreased (n = 4). One-way ANOVA, mean ± SEM.