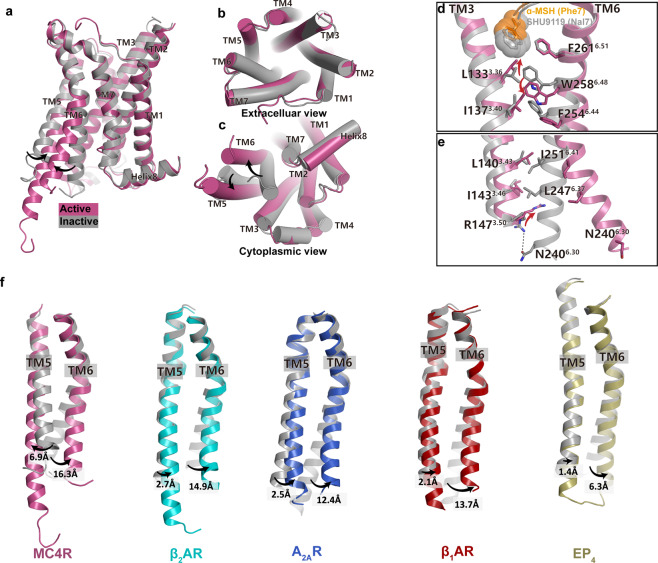
Fig. 6. Activation mechanism of MC4R.
a–c Superposition of the α-MSH-activated MC4R (plum) with the antagonist (SHU9119)-bound MC4R (gray) (PDB: 6W25). Side view (a); extracellular view (b); cytoplasmic view (c). d, e Close-up views of the conformational changes of the crucial residues involved in MC4R activation. f Structure comparisons of TM5 movements among peptide receptors during activation. Inactive and active MC4R, gray and plum; inactive and active β2AR, gray (PDB: 6PS6) and cyan (PDB: 3SN6); inactive and active A2AR, gray (PDB: 6LPJ) and blue (PDB: 6GDG); inactive and active β1AR, gray (PDB: 3ZPQ) and red (PDB: 7JJO); inactive and active EP4, gray (PDB: 5YWY) and yellow (PDB: 7D7M).