Fig. 4. DNA damage repair pathway and the mechanism of PARP inhibitors.
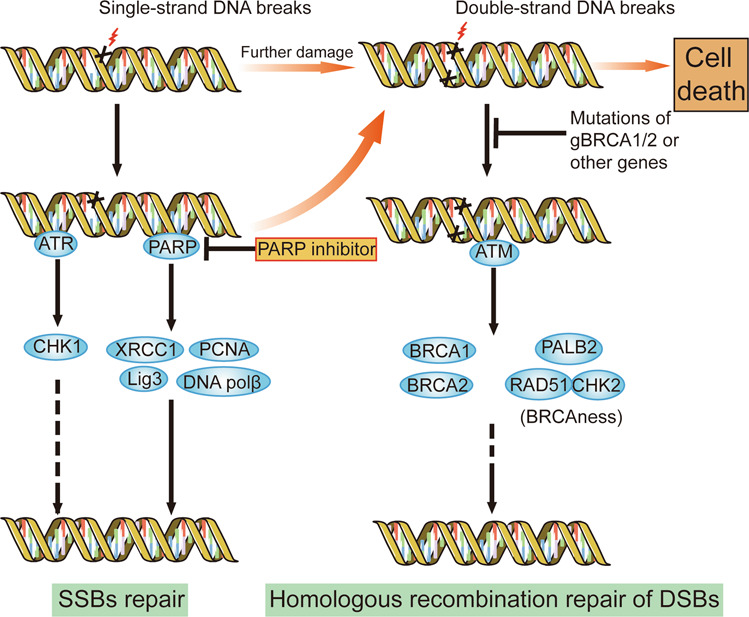
DNA damage repair mainly includes the repair of DSBs and SSBs. PARP and ATR/CHK1 are responsible for SSB repair, while ATM, BRCA1/2 and other BRCAness-related genes are necessary for the homologous recombination repair of DSBs. PARP inhibitors block the repair of SSBs and increase DSBs. Mutations in germline BRCA1/2 or other BRCAness-related genes impair the homologous recombination repair of DSBs, leading to the accumulation of DSBs. The dysfunction of two pathways causes synthetic lethality, genomic instability and cell death.
