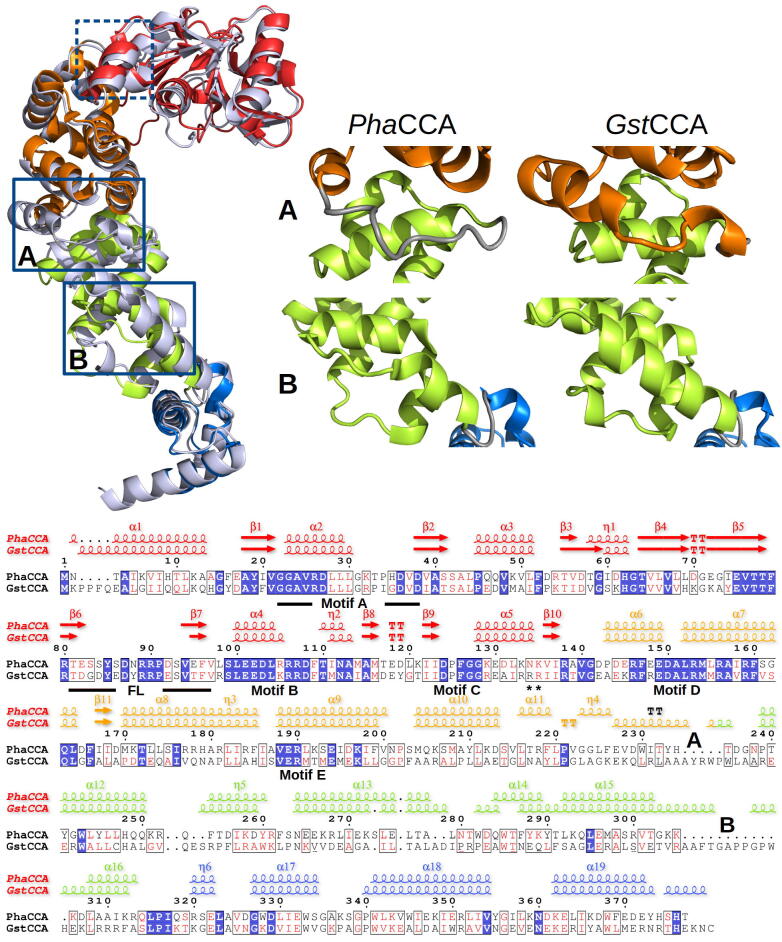
Fig. 3.
Structural adaptations in the psychrophilic CCA-adding enzyme. On the left, the structural alignment of the PhaCCA enzyme (with its domains colored as in Fig. 1) and its thermophilic homolog GstCCA [20] depicted in light blue, reveals typical cold adaptations in its structure. Examples of shorten alpha-helical elements in PhaCCA are boxed in blue (the dashed box highlights helix α5 in motif C discussed in Fig. 5). As illustrated by the close-up views on the right, the helix α11 in region A at the junction of the neck and body is replaced by a loop, while in region B in the body domain helices α15-16 are drastically reduced. These variations in helical regions can be easily spotted in the 2D structure elements presented above the sequence alignment for each structure (see labels A, B). Strictly conserved residues are highlighted in blue, similar residues in red. Catalytic core motifs A to E and the flexible loop (FL) are indicated. Asterisks indicate helix-capping residues R137 and R138 of GstCCA. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)