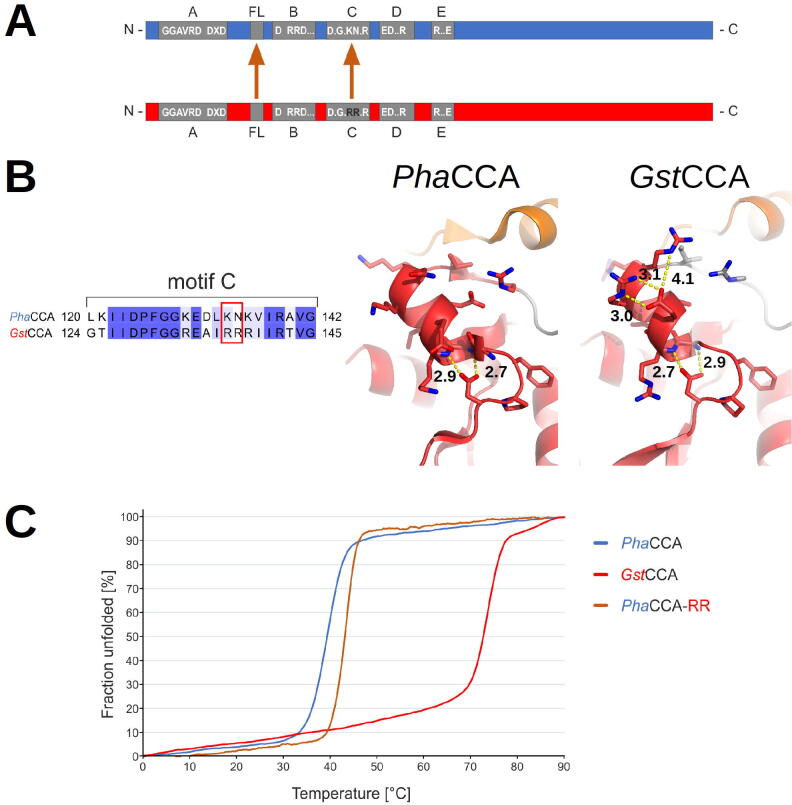
Fig. 5.
Replacement of flexible elements in PhaCCA by their thermophilic counterparts. A) Bar diagrams of PhaCCA (blue) and GstCCA (red). Elements of the catalytic core are indicated in grey. In PhaCCA, the flexible loop (FL) and motif C were replaced by the corresponding regions of GstCCA. B) In GstCCA, helix α5 in motif C (see Fig. 3) carries two R residues that are absent in PhaCCA (left panel). This arginine pair stabilizes an alpha-helical element by a C-terminal helix-capping (right panel). Note the presence of a conserved N-terminal helix-capping involving a strictly conserved aspartic acid of motif C. C) Thermal unfolding of CCA-adding enzymes and PhaCCA with introduced arginine positions involved in C-terminal helix-capping. With a melting temperature of approximately 39 °C, PhaCCA is a true psychrophilic protein (blue). Introducing the helix-capping RR pair increases the melting temperature of PhaCCA–RR to 43 °C (brown). GstCCA shows a typical thermophilic profile and melts at 73 °C (red). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)