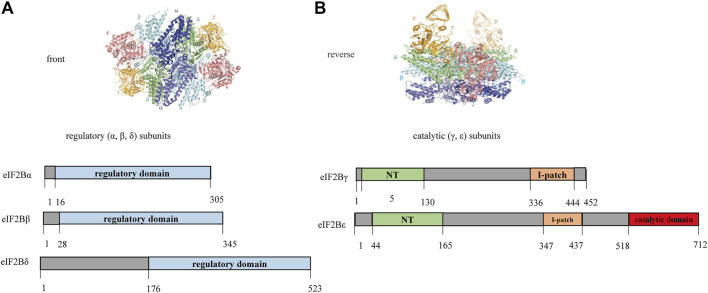
FIGURE 2.
Schematic diagram of the homologous structure of human eIF2B (Kashiwagi et al., 2016). The eIF2B decamer is a heterodimer structure composed of regulatory (α, β, δ) and catalytic (γ, ε) subunits. The γ and ε subunits have two homology domains, the first is NT domain which sequence similarities with nucleotidyl transferases (shown in green in 5–130 amino acids of elF2Bγ and 44–165 amino acids of elF2Bε); the second is I-patch domain which has sequence similarities with acyl transferases (shown in yellow in 336–444 amino acids of elF2Bγ and 347–437 amino acids of elF2Bε), which have approximate hexad spacing of the hydrophobic branched-chain amino acids isoleucine (Ile), valine (Val), and leucine (Leu). The catalytic domain is located at the C-terminus of eIF2Bε(shown in red in 518–712 amino acids of eIF2Bε).