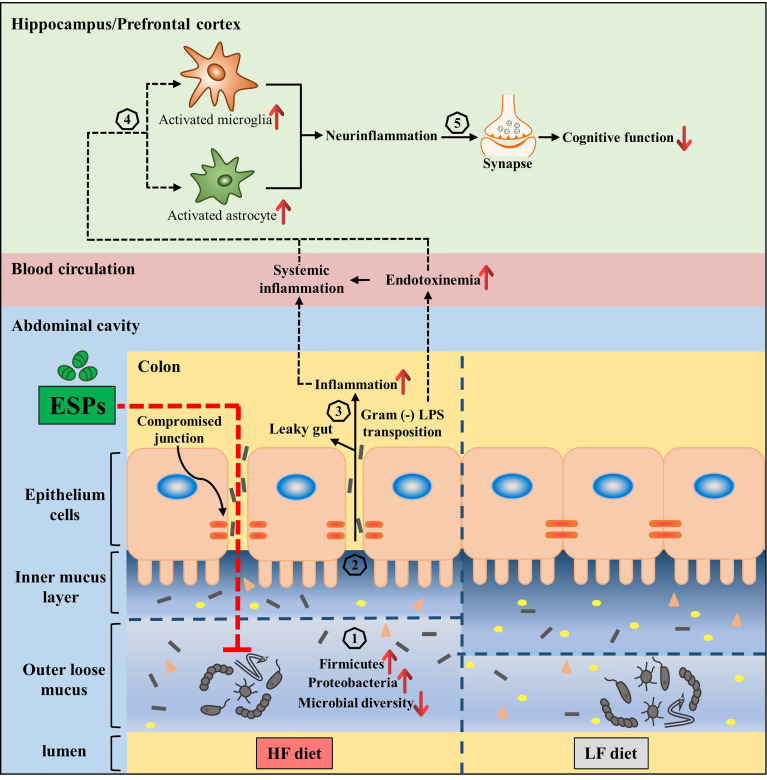
Figure 7.
Interplay between the microbiota and gut-brain axis in high-fat diet and ESPs intervention. Gut microbiota regulates the gut-brain axis to maintain good health, while its alteration (increased of Firmicutes and Proteobacteria, decrease of Bacteroidetes and microbial diversity) due to HF diet is related to obesity, which has adverse consequences on cognition (Steps 1–5). ESPs supplementation is thought to decrease Firmicutes and Proteobacteria, while increasing the microbial diversity (1), thereby maintaining the gut mucus and epithelial integrity as well as immune homeostasis (2); this attenuates the translocation of LPS (3), which decreases the peripheral inflammatory tone and inhibits the activation of microglia and astrocytes, causing neuroinflammation (4) and synaptic damage in the central nervous system (5). Therefore, the supplementation of ESPs has a beneficial impact on cognition via restoration of the gut microbiota and its regulatory role in the gut-brain axis.