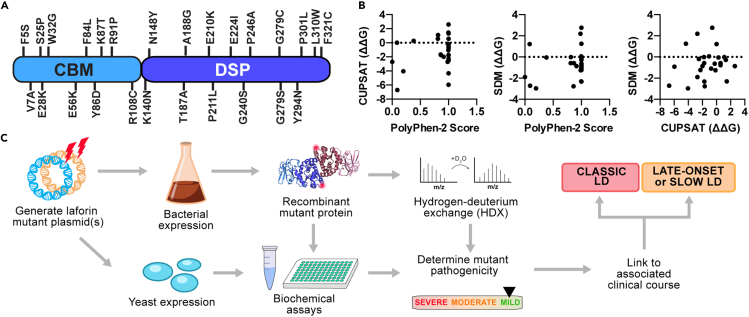
Figure 1.
Pathogenicity predictions and a biochemical pipeline for EPM2A missense mutations
(A) LD missense mutations selected for study are shown mapped to the primary sequence of laforin.
(B) Correlation analysis between PolyPhen-2 pathogenicity score and ΔΔG (kcal/mol) predictions by CUPSAT and SDM for the 26 mutations selected for analysis (see Table 2).
(C) Empirical pipeline for characterizing missense mutations in vitro. The mutations were introduced into bacterial and yeast expression plasmids. Bacterially purified recombinant protein was used for biochemical assays and hydrogen deuterium exchange (HDX) studies. Yeast two-hybrid assays were performed to study laforin interactions with binding partners. The biochemical profile of the mutant was then compiled to determine the severity of the mutation, which is then linked to the clinical course of the patient.