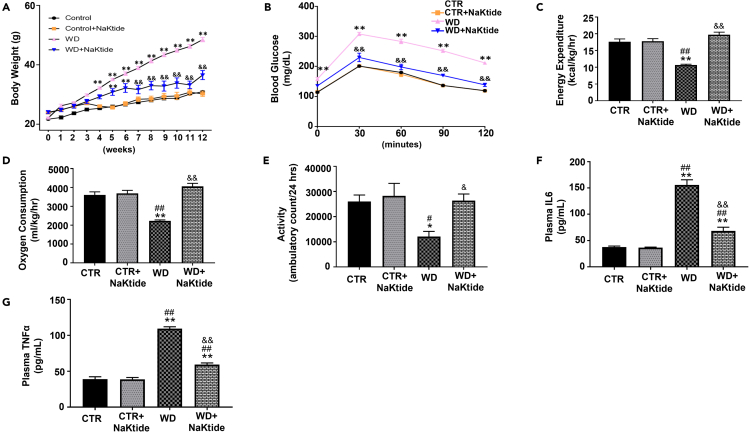
Figure 1.
Doxycycline induced adipocyte-specific NaKtide expression improves adiposity, metabolic imbalance, locomotion and systemic inflammation in mice fed a WD
(A and B) (A) Body weight over the period of 12 weeks. Statistical analysis by two-way ANOVA, where (B) Glucose tolerance test.
(C–G) (C) Energy Expenditure, (D) Oxygen Consumption and (E) Locomotion determined by 48 h CLAMS assessment. Plasma levels of inflammatory markers (F) IL-6 and (G) TNFα. Results are expressed as means ± SEM. N = 6–10/group. Statistical analysis by two-way ANOVA for Panel (A and B), one-way ANOVA for Panel (C – G), multiple comparison using Tukey's test, where ∗p < 0.05 vs. CTR, ∗∗p < 0.01 vs. CTR, #p < 0.05 vs. CTR + NaKtide, ##p < 0.01 vs. CTR + NaKtide, &p < 0.05 vs. WD, &&p < 0.01 vs. WD. Groups: CTR (normal chow diet); CTR + NaKtide (normal chow diet with doxycycline inducible adipocyte specific NaKtide); WD (Western diet); WD + NaKtide (western diet with doxycycline inducible adipocyte specific NaKtide).