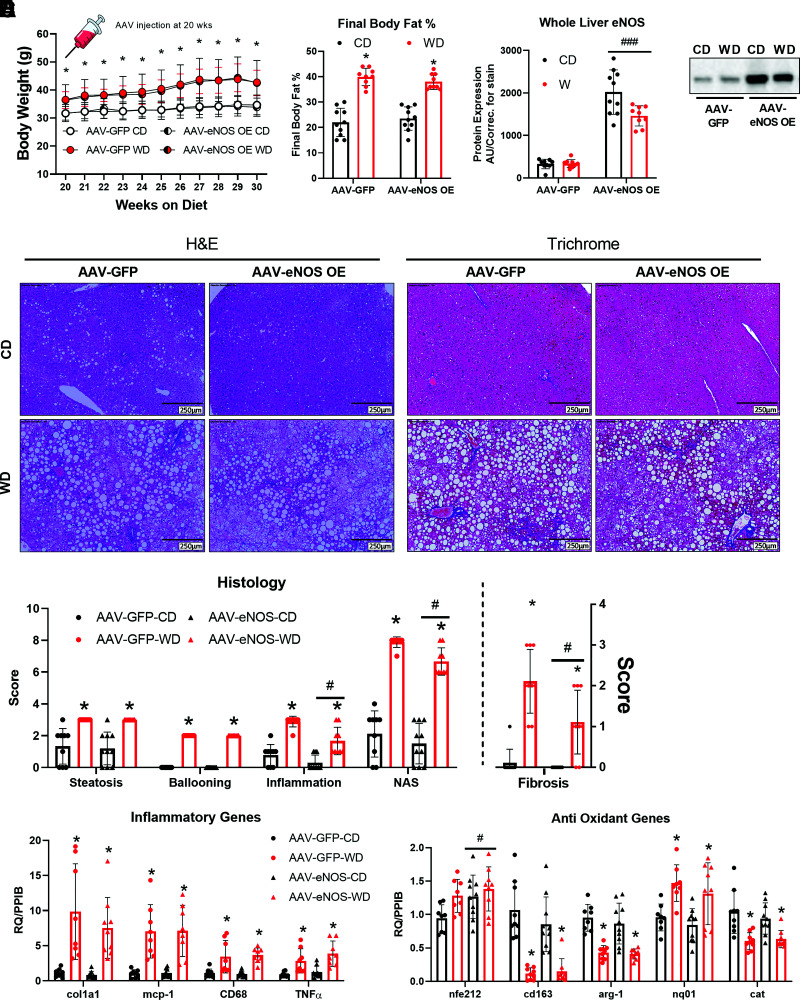
Figure 6.
Long-term hepatocellular eNOS overexpression attenuates WD-induced NASH. C57BL/6J mice were randomized to receive either a CD or WD for 20 weeks, then further randomized to receive either an AAV8-TTR-eNOS overexpression virus or AAV8-TTR-GFP at the 20-week mark, while the body weights were recorded until 30 weeks of age (n = 10/group). A: Body weight over time. B: Final body fat % (n = 10/group). C: Whole-liver protein expression of eNOS confirming the viral overexpression (n = 10/group), and the representative Western blot image. D: Representative liver H&E and trichrome staining from the indicated mice at 30 weeks of age. E: Histological and fibrosis scoring based on H&E and trichrome images (n = 8/group). F: mRNA expression of markers of hepatic inflammatory and antioxidant genes (n = 9–10/group). Data are presented as mean ± SD. *Main effect of diet (P < 0.05 vs. CD), #P < 0.05, and ###P < 0.001, main effect of overexpression vs. AAV-GFP. AU/correc., arbitrary units/correction; CD, control diet; H&E, hemotoxylin-eosin; NAS, NAFLD activity score; RQ/PPIB, relative quotient/cyclophilin B; WD, Western diet.