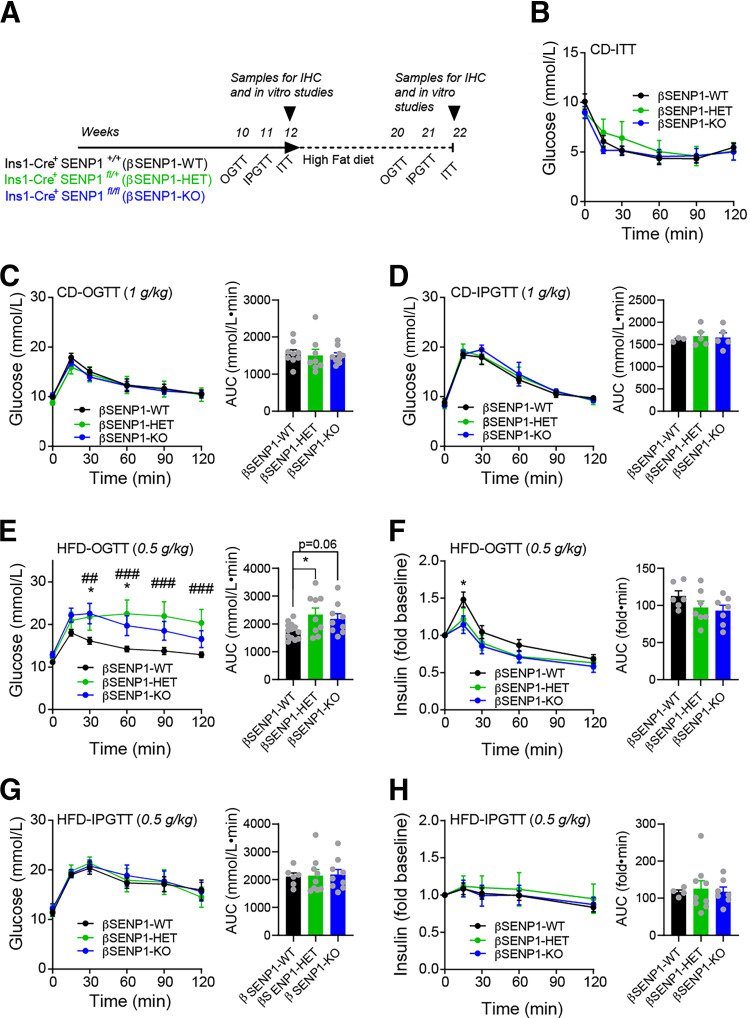
Figure 5.
βSENP1-KO worsens oral, but not IP, glucose tolerance following HFD. A: Schematic diagram of experiments on CD and HFD. B: ITT of male βSENP1-WT, -HET, and -KO mice on CD (n = 6, 6, and 6 mice). C: OGTT of male βSENP1-WT, -HET, and -KO mice on CD (n = 9, 8, and 9 mice). D: IPGTT of male βSENP1-WT, -HET, and -KO mice on CD (n = 3, 5, and 5 mice). E and F: OGTT of male βSENP1-WT, -HET, and -KO mice following HFD (n = 13, 9, and 9 mice) (E) and associated plasma insulin responses (n = 6, 7, and 7 mice) (F). G and H: IPGTT (0.5 g/kg) of male βSENP1-WT, -HET, and -KO mice after HFD (n = 6, 9, and 9 mice) (G) and associated plasma insulin responses (n = 4, 9, and 7 mice) (H). Data are mean ± SEM and were compared using one-way or two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni posttest. *P < 0.05 between βSENP1-WT and βSENP1-KO; ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 between βSENP1-HET and βSENP1-WT, unless otherwise indicated. AUC, area under the curve; IHC, immunohistochemistry.