Figure 3.
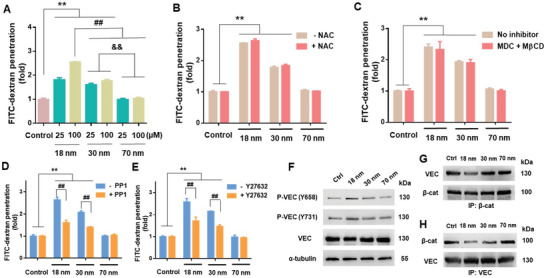
Endothelial leakiness induced by AuNPs was dose‐dependent but endocytosis‐independent, and required activation of VE‐cadherin signaling. A) Transwell assay revealed dependence of NanoEL on the size and concentration of the AuNPs (incubation: 1 h). B) No significant differences occurred in FITC‐dextran penetration across endothelial barriers exposed to AuNPs (100 × 10−6 m, 1 h) with or without prior antioxidant NAC (10 × 10−3 m) treatment (1 h). C) Endocytosis inhibitors (5 × 10−3 m MβCD and 10 × 10−6 m MDC) supplied 1 h prior to AuNP treatment (100 × 10−6 m) did not result in a significant reduction in FITC‐dextran penetration. D) Degree of NanoEL induced by AuNPs (100 × 10−6 m, 1 h) was significantly reduced through pre‐treatment with Src kinase inhibitor, PP1 (10 × 10−6 m, 1 h). E) Pre‐treatment with RhoA kinase inhibitor Y27632 (10 × 10−6 m, 1 h) led to a significant reduction in NanoEL induced by AuNPs (100 × 10−6 m, 1 h). F) Immunoblotting revealed activation of VE‐cadherin (VEC) signaling when exposed to the AuNPs (100 × 10−6 m, 1 h). Phosphorylation of VEC at residues 658 (P‐VEC(Y658)) and 731 (P‐VEC(Y731)) increased with decreasing size of AuNPs. G,H) Immunoprecipitation of β‐catenin (β‐cat) revealed decreased interactions between VEC and β‐cat following cell exposure to the AuNPs (100 × 10−6 m, 1 h). The reverse immunoprecipitation of VEC similarly revealed a decreased association between VEC and β‐cat. Data are presented as mean ± SD, where n = 3, analyzed via two‐way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparison tests, and **, ##, & & all denote P < 0.001 between the various compared groups.
