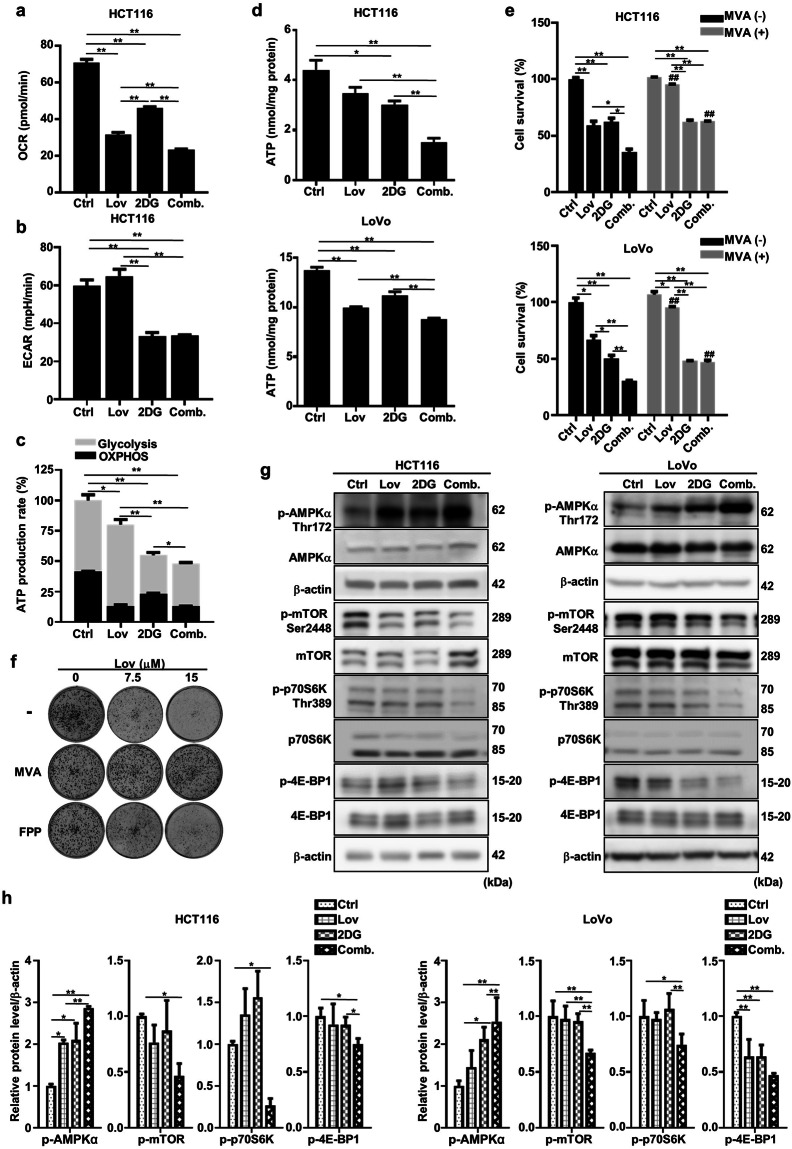
Fig. 4. The combination of lovastatin and 2DG depletes the intracellular ATP level and regulates the AMPK/mTOR pathway.
After 48 h of exposure to lovastatin (15 μM) and 2DG (5 mM) alone or in combination, the oxygen consumption rate (a) and extracellular acidification rate (b) of HCT116 cells were measured on a Seahorse XFp analyzer. c The relative ATP production rate by glycolysis and OXPHOS was calculated by measuring oxygen consumption and extracellular acidification with a Seahorse XFp analyzer (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus total relative ATP production rate). d After treatment with lovastatin (15 μM) and 2DG (5 mM) alone or in combination for 24 h, the intracellular ATP concentrations in HCT116 and LoVo cells were measured. e HCT116 and LoVo cells were cultured with lovastatin (15 μM) and 2DG (5 mM) alone or in combination for 72 h in either the presence or absence of 200 mM mevalonate, and cell proliferation was determined. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. ##P < 0.01 vs corresponding MVA (-) group. f HCT116 cells were cultured with lovastatin at the indicated concentrations in the presence or absence of 200 μM mevalonate/10 μM farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), and colony formation was determined. g Representative immunoblots of AMPKα, p-AMPKα Thr172, mTOR, p-mTOR Ser2448, p70S6K, p-p70S6K Thr389, 4E-BP1 and p-4E-BP1 from the HCT116 and LoVo cells treated with lovastatin (15 μM) and 2DG (5 mM) alone or in combination for 48 h. β-actin served as a loading control. h Quantified data of (g). All data are from at least three independent experiments.