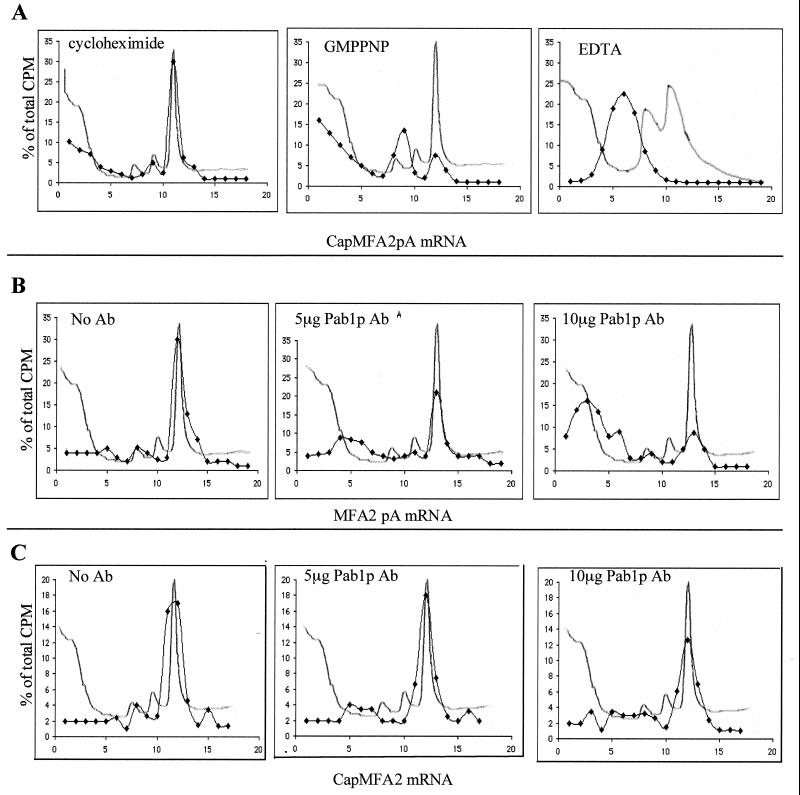
FIG. 7.
(A) Separation of translation initiation intermediates by centrifugation through sucrose gradients. Translation extracts from wild-type strains containing the indicated inhibitors were programmed with 35S-labeled CapMFA2pA mRNA. Formation of initiation complexes was analyzed on 10 to 30% sucrose gradients. Sedimentation proceeded from left to right. OD260 profiles were monitored to determine positions of 40S, 60S, and 80S particles (line without symbol). Radioactivity was determined in each fraction by direct counting, and data are expressed as the percentage of total radioactivity in the gradient (⧫). Labeled RNA cosedimented with the 80S initiation complex in the presence of cycloheximide, the 48S preinitiation complex in the presence of GMPPNP, and free mRNP in the presence of EDTA. (B and C) Pab1p antibodies inhibit 40S ribosomal subunit binding to MFA2pA mRNA but not to CapMFA2 mRNA. Translation extracts from wild-type cells containing the indicated amounts of Pab1p antibody were programmed with MFA2pA mRNA (B) or CapMFA2 mRNA (C) in the presence of cycloheximide and analyzed on sucrose gradients as described for panel A. Ab, antibody.