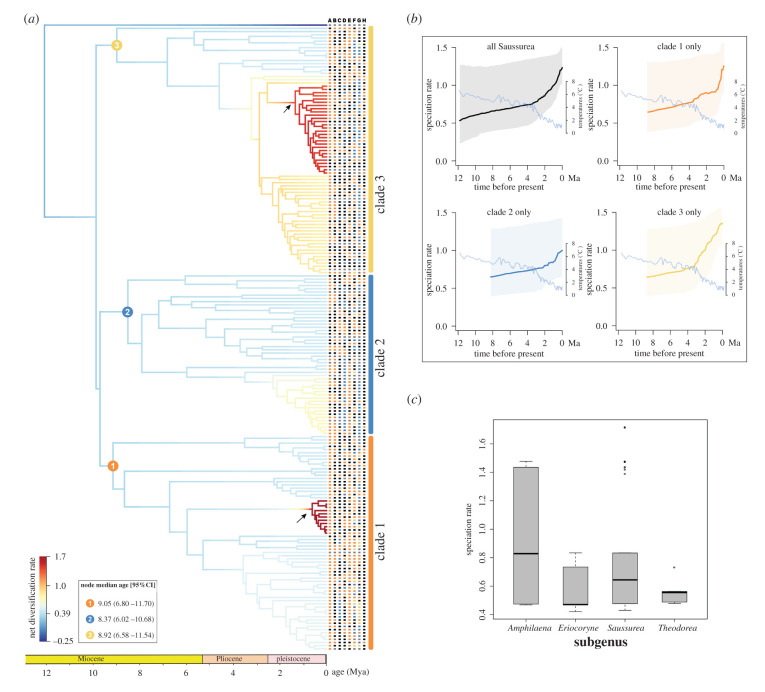
Figure 1.
Diversification dynamics of Saussurea inferred from BAMM analysis. (a) Two shifts in DRs (represented by arrows). The timing for the origins of the three major clades of the genus is provided. The character states of eight morphological traits are plotted on the tree, as follows. A: stemless (black) versus stemmed (orange), B: stem glabrous (black) versus densely hairy (orange), C: leaf margin entire (black) versus pinnately lobed (orange) versus both types (blue), D: leaves glabrous (black) versus sparsely hairy (orange) versus densely hairy (blue), E: capitula solitary (black) versus numerous (orange), F: phyllary in less than 5 (black) versus 5 (orange) versus 6 (blue) versus greater than 6 (yellow) rows, G: phyllary glabrous (black) versus sparsely hairy (orange) versus densely hairy (blue) versus appendaged (yellow) and H: the absence (black) versus presence (orange) of leafy bracts. Unknown character states are coloured in grey. (b) Rates-through-time plots of all Saussurea species and three main clades separately, with trends in global climate change over 12 million years depicted. (c) BAMM tip rates of four morphology-based subgenera of Saussurea. (Online version in colour.)