Figure 1.
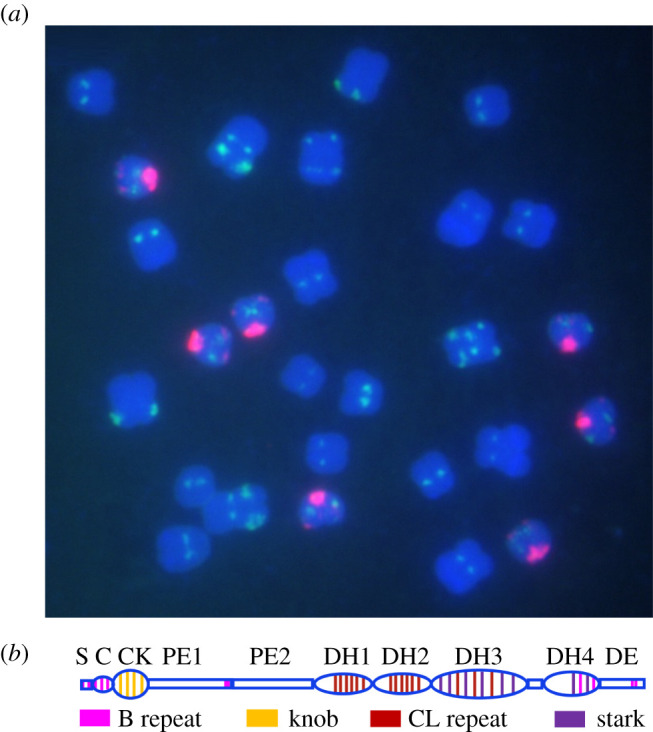
The maize B chromosome. (a) Mitotic metaphase spread of a line with seven B chromosomes (magenta). The magenta signal identifies the ZmBs (B specific repeat) in the centromere and short arm with a minor representative at the distal tip of the B long arm. Green signal identifies two chromosomal features, namely the CentC centromeric satellite and TAG microsatellite clusters. The green signal on the B chromosome represents CentC clusters, which have no centromere activity [26]. DAPI stains the chromosomes (blue). (b) Schematic view of the acrocentric maize B chromosome at pachynema of meiosis. The chromosome is divided into the B short arm (S), B centromere (C), centromeric knob (CK), proximal euchromatin (PE1-2), four blocks of distal heterochromatin (DH1-4) and the distal euchromatin (DE). Four representative repeats on the B chromosome including the B-specific repeat ZmBs, knob-180, CL-repeat and Stark repeat cluster are colour coded along with the length of the chromosome. Knob is present in the centromeric knob region. CL repeat is present at DH1, 2 and 3. The Stark repeat is present in most of DH3 and the distal portion of DH4.
