Figure 1:
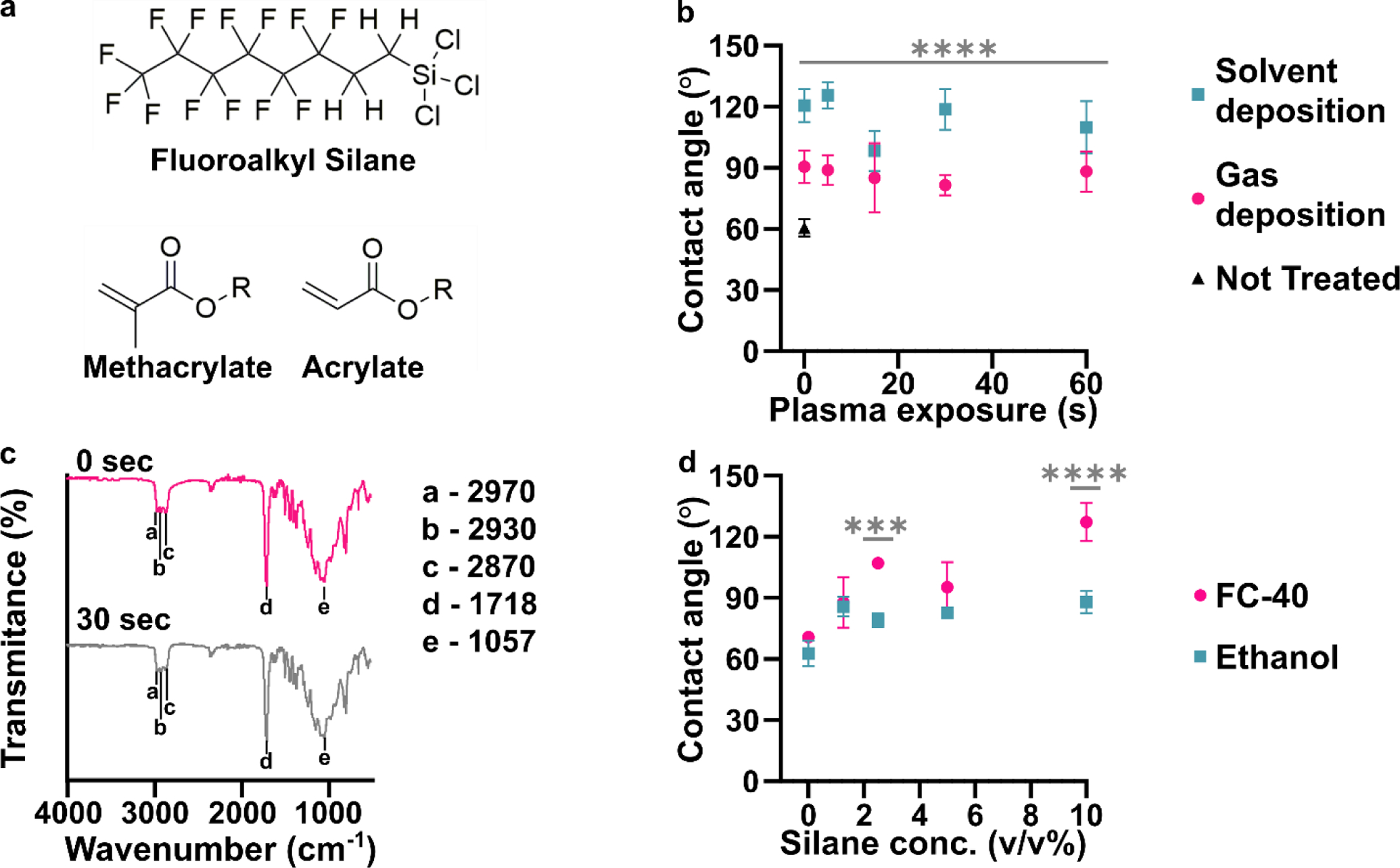
Effects of plasma treatment and silanization on the chemistry and hydrophobicity of DLP printed pieces. (a) Chemical structures of the fluoroalkyl silane and monomer acylate and methacrylate base used for many resin formulations. (b) Air/water contact angles of BV-007A after silanization by solution-phase (blue squares, FC-40 solvent) or gas-phase (pink dots) deposition after varied times of treatment with air plasma (n=3, mean ± std dev). The black triangle represents printed BV-007A pieces that received neither plasma treatment nor any silane treatment. Two-way ANOVA for solution vs gas-phase silanization (**** p<0.0001). (c) ATR-FT IR spectrum of the BV-007A surface with no exposure to air plasma (pink) and after 30 s plasma treatment (grey), without silanization. Spectra are offset to display spectral features. (d) Air/water contact angles of BV-007A surface after solution-phase silanization in FC-40 (pink dot) or ethanol (blue square). Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons to compare between solvents (****p <0.0001, *** p<0.001).
