Fig. 7.
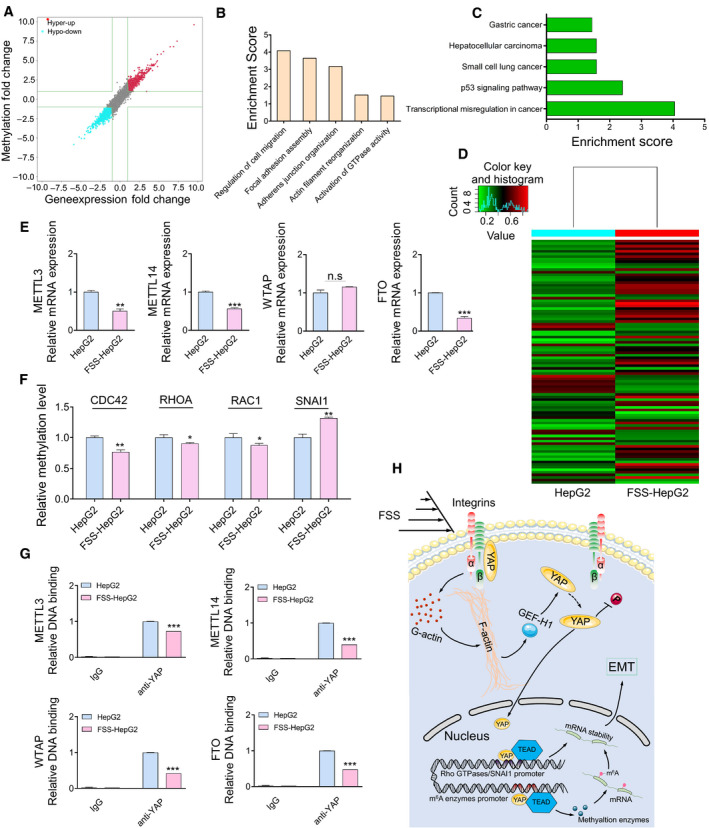
YAP modulates the m6A RNA methylation of EMT ‐related genes. (A) The distribution of transcript with a significant change in both m6A level and expression in the comparison of FSS‐HepG2 with HepG2 cells. (B) Major enriched and meaningful BP terms of m6A peaks transcripts. (C) Significantly enriched pathways of m6A peak transcripts. (D) Hierarchical clustering analysis of the differentially methylated mRNA. (E) qPCR analysis of METTL3, METTL14, WTAP and FTO in HepG2 and FSS‐HepG2 cells. (F) The methylation level analysis of EMT‐related genes identified in m6A‐mRNA microarray data. (G) ChIP‐qPCR showing fold changes of the association of YAP with the promoter of METTL3, METTL14, WTAP and FTO. (H) FSS induces YAP separation from integrin β subunits. Integrin β subunits transmit the biomechanical signal to F‐actin, which results in translocation of YAP to the nucleus through GEF‐H1. The activated nuclear YAP triggers EMT through transcriptional and post‐transcriptional modification of EMT‐related genes. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3, by two‐tailed unpaired t‐test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s. denoting no significance).
