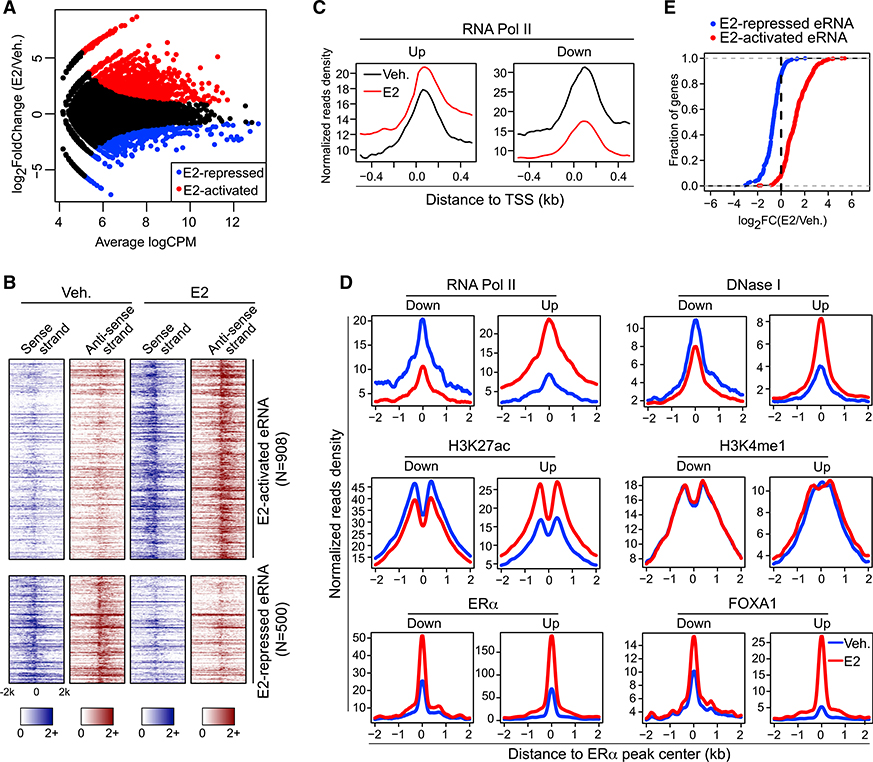
Figure 1. Two Groups of ERα-Bound, eRNA-Producing Enhancers Were Identified, which Respond Differentially to E2 Treatment.
(A) MA plot of ERα-localized enhancers that generate differentially expressed (false discover rate [FDR] ≤ 0.05 and fold change ≥ 1.5) eRNAs upon E2 treatment.
(B) Heatmaps of GRO-seq signals for sense- and antisense-strand eRNAs under vehicle (Veh.) or estrogen treatment (E2) condition.
(C) E2-induced changes in the Pol-II-binding intensities around transcription start sites (TSSs) of coding genes whose promoters showed detectable ChIA-PETsignals with E2-upregulated (Up) or E2-downregulated (Down) enhancers.
(D) Aggregate plots showing the binding intensities of indicated factors at E2-upregulated (Up) and E2-downregulated (Down) enhancers in the absence (Veh.) orpresence (E2) of estradiol.
(E) Cumulative distribution of E2-stimulated expression changes of coding genes nearest to E2-activated or E2-repressed eRNAs. The differential expression between vehicle (Veh.) and E2 treatment conditions was presented as log2(fold change) (log2FC).
Also see Figure S1.