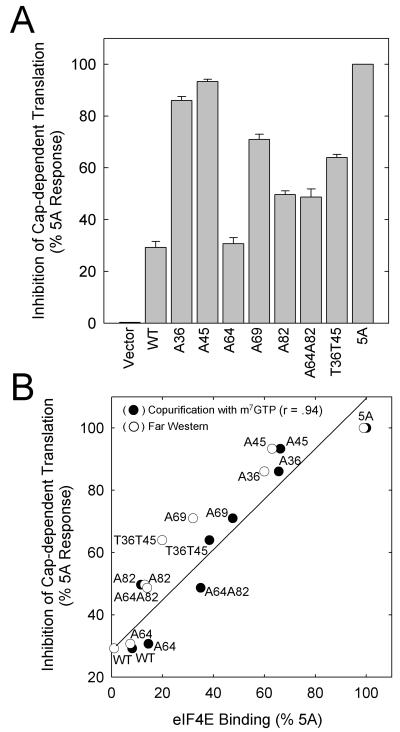
FIG. 8.
Effect of mutations on cap-dependent mRNA translation. HEK293 cells were cotransfected with pRLIRESFL and the PHAS-I expression vectors. The cells were incubated as described in the legend to Fig. 7 before the activities of the two luciferases were measured. None of the PHAS-I proteins decreased firefly luciferase activity, which was used to correct for small differences in the transfection efficiency of the reporter construct among samples. Approximately equal amounts of the different PHAS-I proteins were expressed (see Fig. 7B, for example). (A) Inhibition of cap-dependent translation resulting from PHAS-I proteins, expressed relative to that produced by 5A PHAS-I (mean values and standard errors from three experiments). (B) Relationship between eIF4E binding and inhibition of cap-dependent mRNA translation. The relative amounts of PHAS-I proteins copurifying with eIF-4E (●) or the relative amounts of FLAG–eIF4E binding (○) from Fig. 7 are plotted against the inhibition of cap-dependent mRNA translation. The line and correlation coefficient (r) were generated by linear regression analysis of translation inhibition versus PHAS-I protein recovered with m7GTP-Sepharose.