Figure 2.
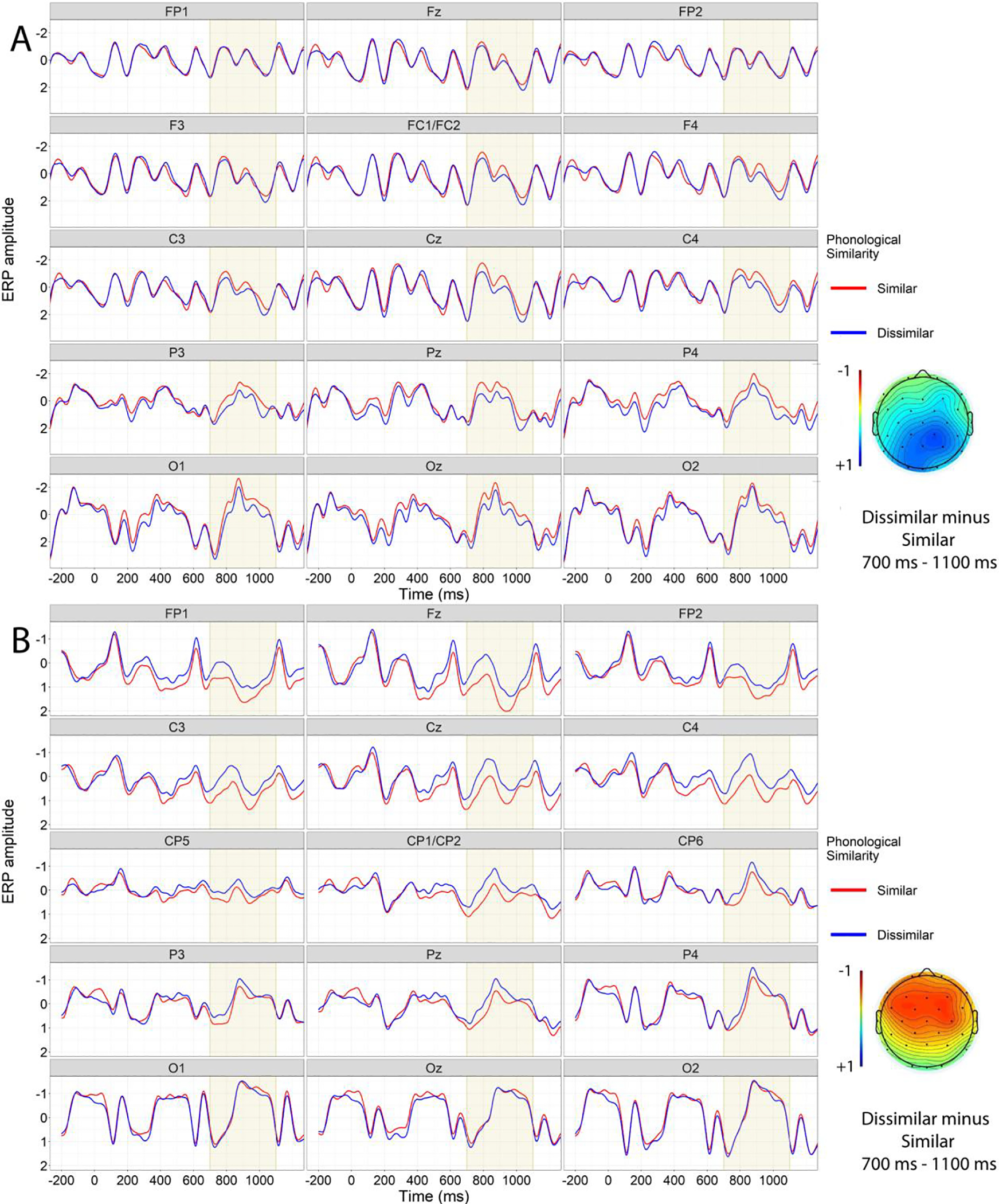
Grand average brain waveforms of younger (Panel A) and older adults (Panel B) time-locked to pronoun onset. The critical time window is highlighted. Relative to pronouns following phonologically dissimilar NPs, pronouns following phonologically similar NPs caused larger parietal negativities for younger adults, but smaller frontal negativities for older adults.
