Figure 2.
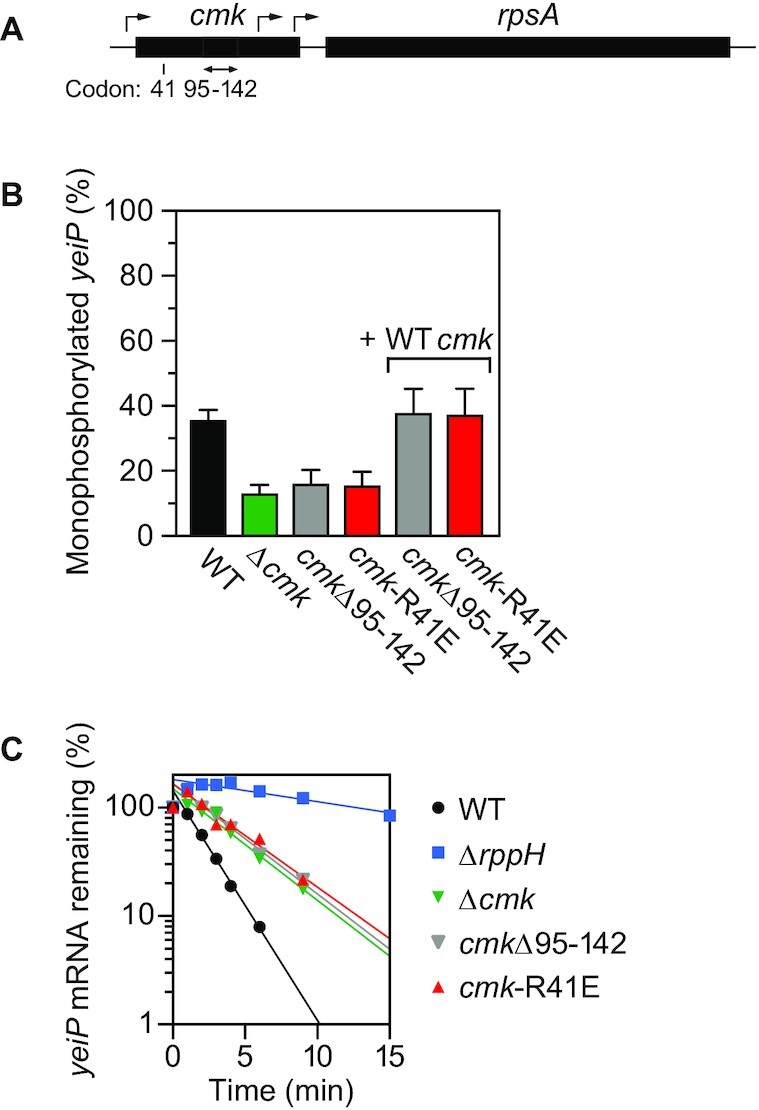
Importance of the catalytic activity of cytidylate kinase for its effect on mRNA degradation. (A) Chromosomal cmk-rpsA locus in E. coli. The location of the cmk-R41E codon substitution is indicated. Black rectangles, cmk and rpsA genes. Bent arrows, transcription initiation sites (37). Double-headed arrow, cmk gene segment spanning codons 95–142. (B) Effect of cmk mutations on the phosphorylation state of yeiP mRNA. The percentage of monophosphorylated yeiP 5′ ends was determined by PABLO, as in Figure 1. + WT cmk, complementation of cmkΔ95–142 and cmk-R41E with a plasmid-borne copy of the wild-type cmk gene. Each value is the average of three biological replicates. Error bars correspond to standard deviations. (C) Effect of cmk mutations on the decay rate of yeiP mRNA. The decay of yeiP mRNA in an isogenic set of E. coli strains was monitored as a function of time after inhibiting transcription with rifampicin, plotted semilogarithmically, and analyzed by linear regression. Representative experiments are shown.
