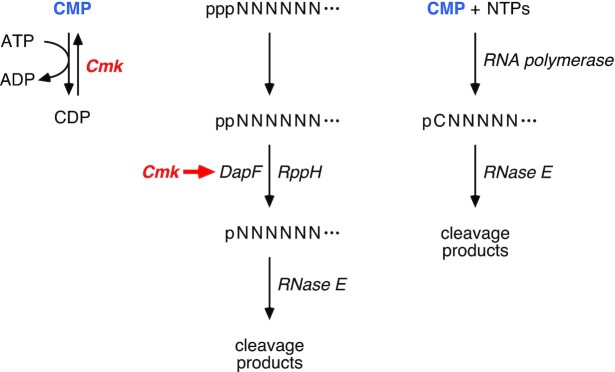
Figure 7.
Cellular functions of cytidylate kinase. (Left) Role of cytidylate kinase (Cmk) in the conversion of CMP to CDP. (Center) Importance of the catalytic activity of cytidylate kinase for enabling DapF to potentiate RppH-mediated 5′ phosphate removal from diphosphorylated RNA as a prelude to rapid endonucleolytic cleavage of the monophosphorylated RNA product by RNase E. Represented by a short red arrow, this stimulatory effect of cytidylate kinase presumably is a direct or indirect consequence of the depletion of one of its substrates or the accumulation of one of its products. (Right) Direct synthesis of monophosphorylated C-initiated transcripts by RNA polymerase when the CMP that accumulates in cells lacking cytidylate kinase activity is incorporated into RNA during transcription initiation. ppp, triphosphate; pp, diphosphate; p, monophosphate. N, RNA nucleotide; C, cytidine nucleoside. Ellipsis, 3′-terminal RNA segment.