Figure 2.
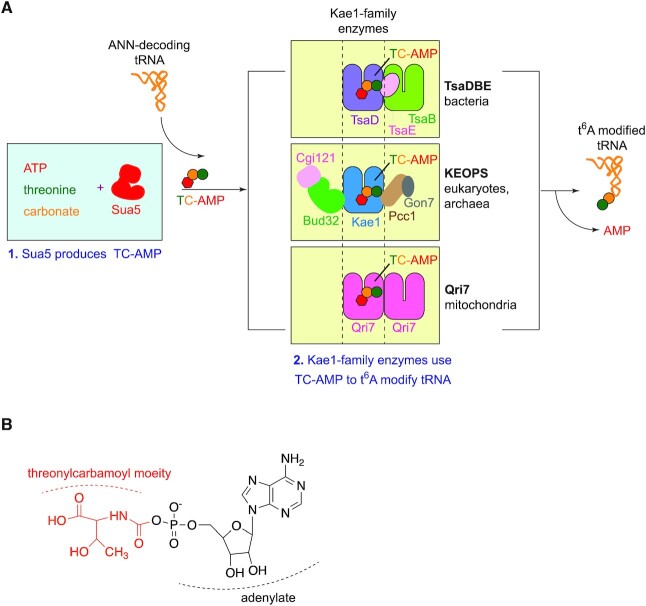
t6A is universally biosynthesized in a two-step reaction by Sua5 and Kae1/TsaD/Qri7 enzymes. (A) Schematic of the universal t6A biosynthesis pathway. Step 1- Sua5 utilizes ATP, threonine and HCO3−/CO2 to catalyze the formation of threonylcarbamoyl adenylate (TC-AMP). Step 2- TC-AMP is used by Kae1/TsaD/Qri7 enzymes to t6A modify ANN-decoding tRNA substrates. (top) TsaD functions with the TsaB and TsaE subunits in bacteria. (middle) Kae1 functions with Cgi121, Bud32, Pcc1 and Gon7 subunits in the cytoplasm in eukaryotes and in archaea. (Bottom) Qri7 functions either as a homo-dimer as shown in figure or as a monomer. (B) Chemical structure of threonylcarbamoyl adenylate (TC-AMP). The threonylcarbamoyl moiety is shown in red and the adenylate is shown in black.