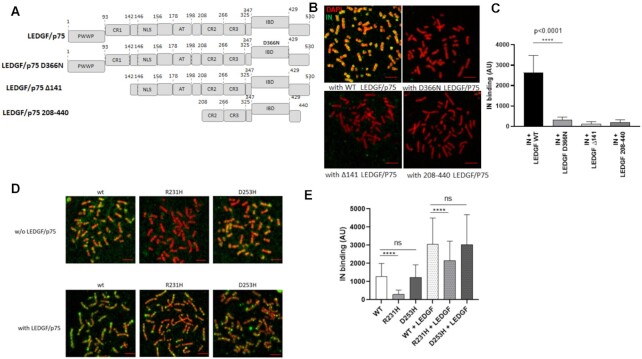
Figure 3.
Effect of LEDGF/p75 and IN carboxyterminal domain mutants on the modulation of HIV-1 IN chromatin binding property. The different constructions used in the experiments are reported in (A). Full length, D366N LEDGF/p75 punctual mutant impaired for binding to HIV-1 IN and truncations deleted for the PWWP chromatin binding domain and AT hook of LEDGF/p75 were compared for their effect on HIV-1 IN binding to chromosomes. The purified LEDGF/p75 mutants were added to HIV-1 IN in the chromatin binding assay and their effects on the anchoring of IN were compared to the one showed by WT protein (B). The total IN binding signal was quantified along chromosomes (here chromosome 1) in the different conditions and are reported in the histogram as means of eight independent set of quantification (between 738 and 954 quantification points) ± SD. Statistics were performed by Student's t-test and the calculated P is reported on the figure (C). WT, R231H and D253D IN proteins were incubated with chromosome spreads in the absence or in the presence of LEDGF/p75 (4nM) and the IN binding to chromatin was monitored by immunofluorescence using anti-IN antibody (D). The intensity of total IF signal has been quantified in each condition using ImageJ software on several chromosomes and reported as IN binding. The data are reported as mean of the quantification of ten chromosomes 1 (1026–1122 quantification points) ± SD. Statistics were performed by Student's t-test and the calculated p is reported on the figure (E). Scale bar = 10 μM.