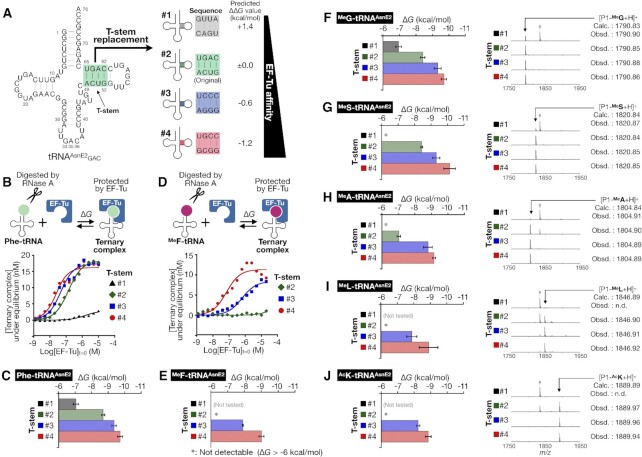
Figure 3.
Reinforcement of EF-Tu affinity of Phe-tRNA and npAA-tRNAs by T-stem engineering. (A) Sequence of the original tRNAAsnE2 (#2) and T-stem variants #1–4. The affinities of tRNA #1–4 were designed to increase as the T-stem number increases from #1 to #4. (B–E) Quantification of the EF-Tu affinities of Phe-tRNAGAC#1–4 (B, C) and MeF-tRNAGAC#2–4 (D, E). Schematic representation of RNase A protection assay, the observed fraction of the ternary complex with the fitting curve to determine the KD value (B, D), and the calculated ΔG value (C, E). Asterisk (*) indicates undetectably weak affinity (ΔG > −6 kcal/mol). Error bar indicates the fitting error. (F–J) The EF-Tu affinities of npAA-tRNA#1–4 and MALDI-TOF MS of P1-npAA examined for MeG (F), MeS (G), MeA (H), MeL (I) and AcK (J). Each dagger peak (†) corresponds to a byproduct containing Ile in place of npAA.