Figure 6.
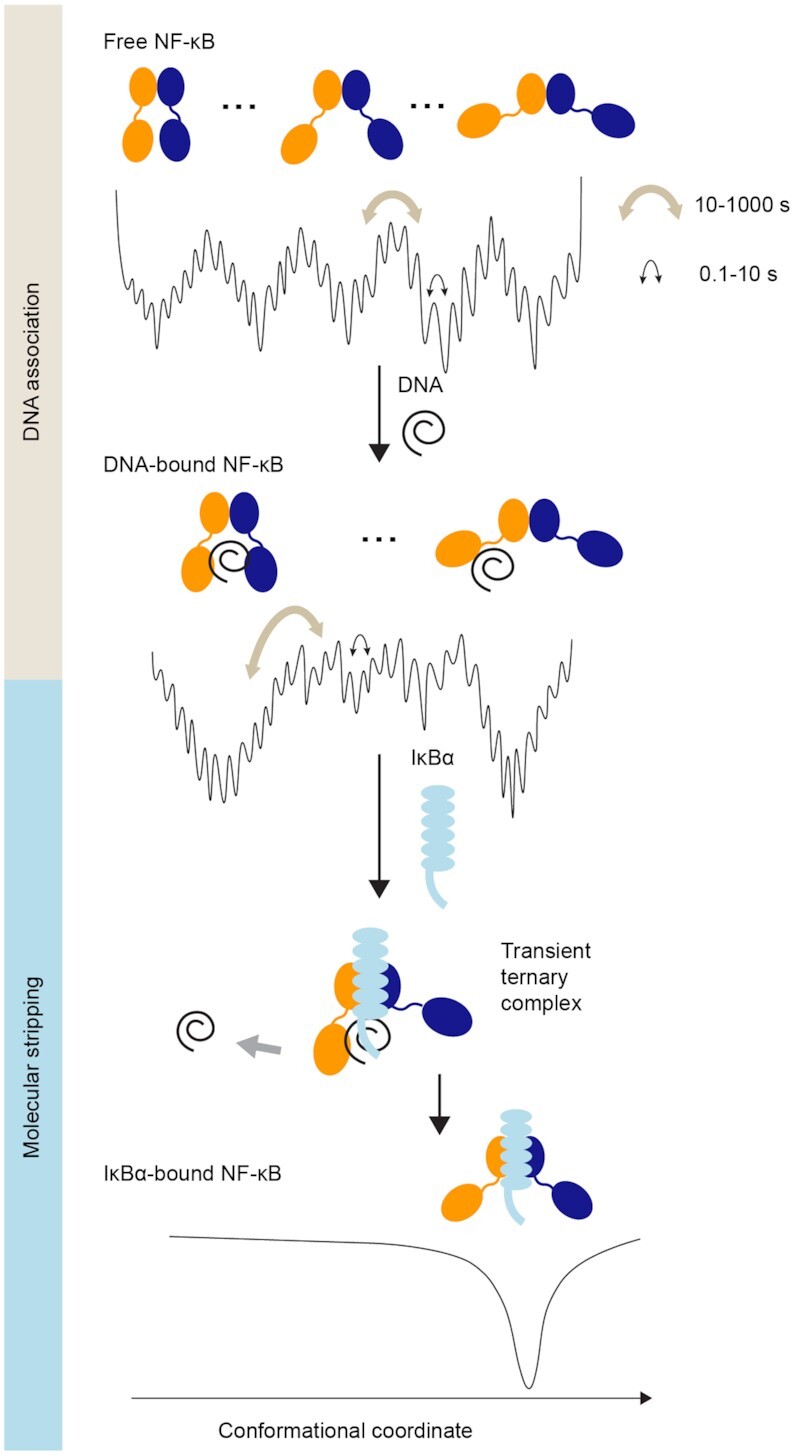
NF-κB utilizes a continuum of binding modes for DNA association and molecular stripping. The energy landscape of free NF-κB is highly rugged and hierarchically organized, resulting in a continuum of conformations interconverting on the subseconds to minutes timescale, comparable to in vivo binding on the seconds timescale. Free NF-κB adopts a broad distribution of conformations, each with a different degree of DNA accessibility. DNA-bound NF-κB also adopts a continuum of distributions, which leads to a continuum of off rates in cells. The two major populations of DNA-bound NF-κB correspond to a fully bound state and a partially bound state; the latter allows the invasion of IκBα to form a ternary complex and eventually strip NF-κB from DNA. Binding of IκBα facilitates DNA dissociation and inhibits DNA binding by inducing a single static conformation in NF-κB where the NTDs are too far apart to both engage DNA.
