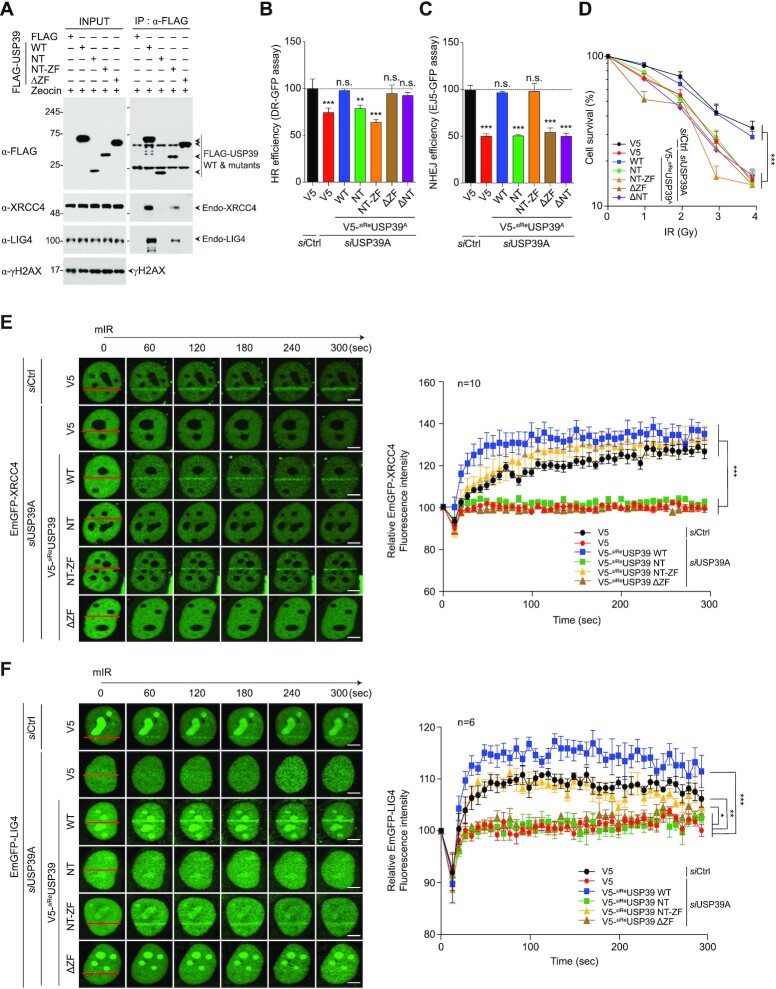
Figure 7.
The ZF domain of USP39 is an essential region for interaction with XRCC4 and LIG4. (A) The ZF domain of USP39 serves as a docking site for the interaction with XRCC4/LIG4 complex. Cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged WT or mutant of USP39 and were subjected to IP with FLAG antibody and then analyzed by immunoblotting. (B and C) Comparative analysis of HR (B) and NHEJ (C) repair activities in USP39 knockdown cells or cells rescued by reintroducing siReUSP39 or deletion mutants. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey Kramer test. (D) A clonogenic cell survival assay was performed using the indicated experimental conditions. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey Kramer test. (E and F) The ZF domain of USP39 is important for recruitment of XRCC4 and LIG4. GFP-tagged XRCC4 or LIG4 were transfected into USP39 knockdown cells along with the indicated siRNA-resistant V5-fused WT or USP39 mutants. Stripe formation by each deletion mutant was monitored (left panels in E and F) and the efficacy of translocation was quantified by Nikon NIS software as indicated (right panels in E and F). Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey–Kramer test. Scale bars, 5 μm. Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments and quantification results represent the mean ± s.e.m. from five cells. ***P ≤ 0.001, **P ≤ 0.01, *P ≤ 0.05. n.s., not significant.