Figure 4.
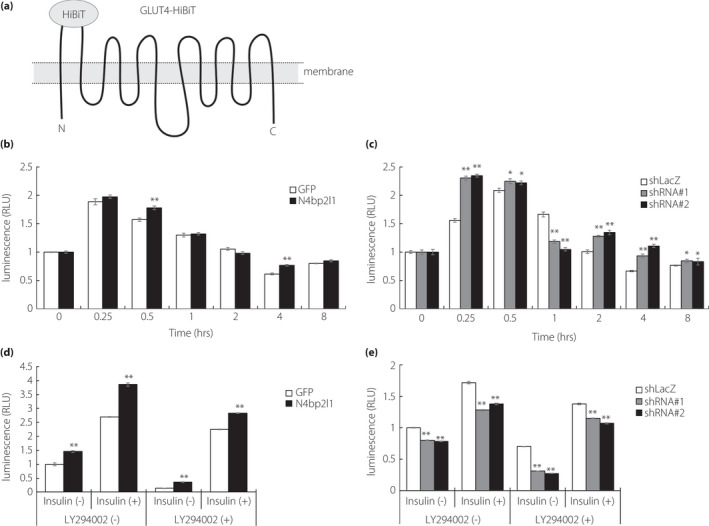
N4BP2L1 affects GLUT4 translocation and is involved in glucose uptake. (a) A schematic diagram of GLUT4‐HiBiT. The N‐ and C‐termini of GLUT4 are in the cytoplasm, and HiBiT is fused to the first extracellular loop of GLUT4. In the presence of insulin, GLUT4‐HiBiT translocates to the cell membrane to promote glucose uptake. GLUT4‐HiBiT can regulate the translocation of the GLUT4 in live cells in real time. (b and c) N4BP2L1 influences GLUT4 translocation in 3T3‐L1 adipocytes. 3T3‐L1 adipocytes were co‐infected with GLUT4‐HiBiT and either GFP or N4bp2l1 adenovirus or either shLacZ or N4bp2l1 shRNA adenovirus. After 48 h, the cells were incubated with or without insulin (1 μM) for each time point. GLUT4‐HiBiT translocation to the cell membrane was measured using a detection reagent containing LgBiT and NanoLuc substrate. n = 3 per group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs GFP or shLacZ. (d and e) N4BP2L1 influences glucose uptake in 3T3‐L1 adipocytes. 3T3‐L1 adipocytes were infected with either GFP or N4bp2l1 adenovirus or either shLacZ or N4bp2l1 shRNA adenovirus. After 48 h, the cells were preincubated with or without LY294002 (50 μM) for 30 min followed by exposure to insulin (1 μM) for a further 1 h. Afterward, glucose uptake assay was performed. n = 3 per group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs GFP or shLacZ.
