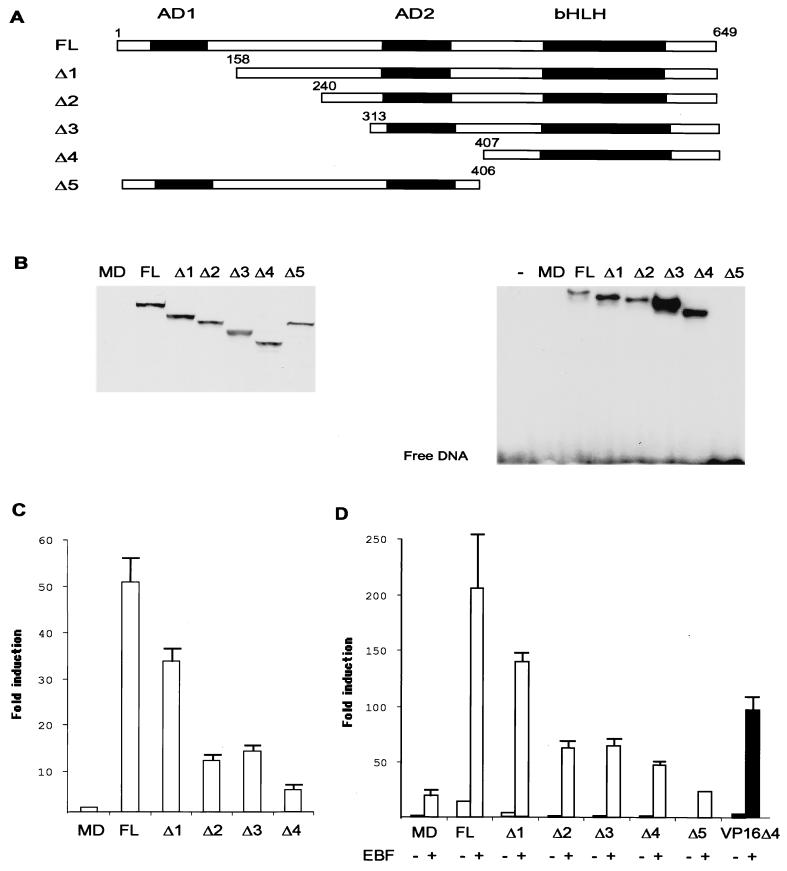
FIG. 3.
The transactivation domains of E47 are essential for full function but not for cooperation with EBF. Panel A shows a schematic drawing of the full-length and truncated E47 proteins that were fused to an amino-terminal 9E10 myc tag. Functional domains in E47 are indicated by black boxes and represent the transactivation domains AD1 and AD2 and the bHLH domain as indicated. The numbers indicate the amino acid positions for the truncations. The figure is not drawn to scale. (B) The left panel shows Western blot analysis with 9E10 anti-myc antibody and 10-μg nuclear extracts from HeLa cells transiently transfected with 800 ng of the indicated E47 protein. The right panel shows an autoradiogram from EMSA using 5-μg nuclear extracts from transiently transfected HeLa cells and an end-labeled oligonucleotide encompassing the μE5 E-box as indicated. (C) Diagram indicating the relative luciferase activity obtained after transient transfections of 200 ng of the λ5 reporter plasmid with 300 ng of E47-encoding plasmids as indicated. The reporter activity obtained with 300 ng of empty expression plasmid was set as one, and the data were calculated from three representative transfection experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (D) Diagram representing the relative luciferase activity obtained when 200 ng of the λ5 reporter plasmid was transfected with 50 ng of E47-encoding plasmids in combination with 150 ng of empty (−) or 9E10-tagged EBF-encoding (+) expression plasmid in HeLa cells. The black bars indicate that these data were collected from an independent transfection experiment. The reporter activity obtained with 200 ng of empty expression plasmid was set as 1, and data are collected from three representative transfections. Error bars indicate standard deviations.