Figure 1.
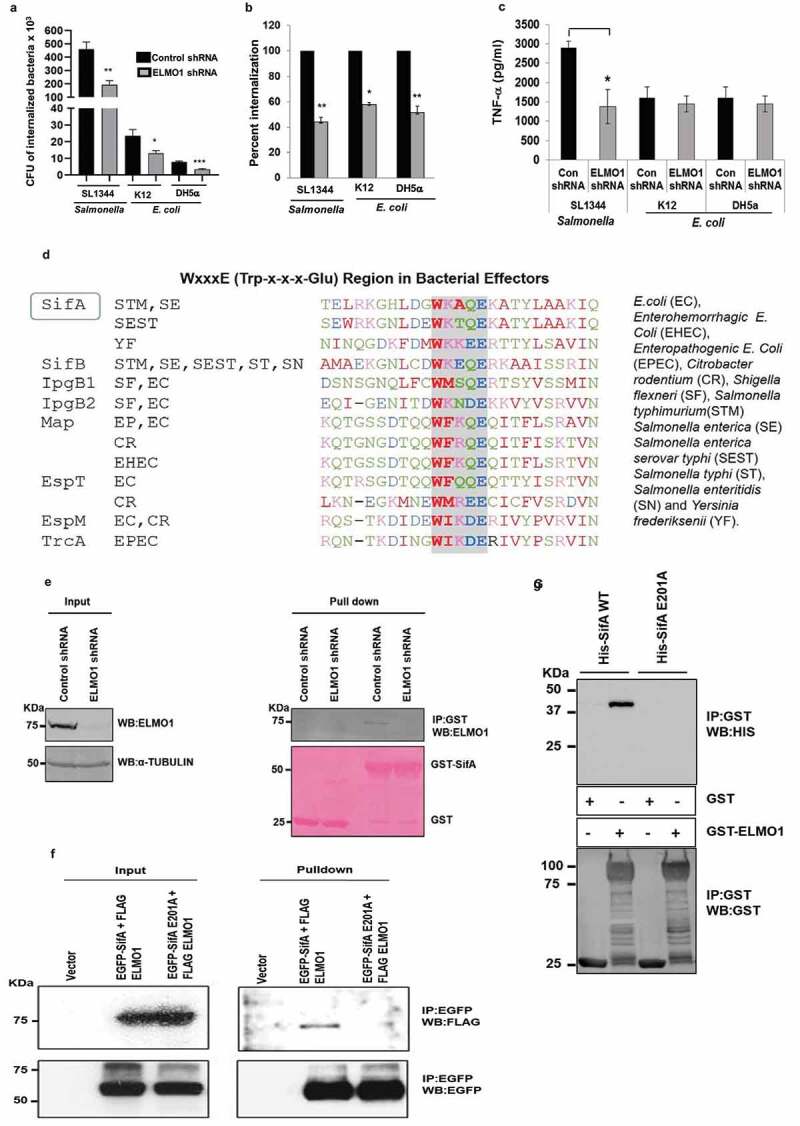
ELMO1 generates a differential immune response between pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria. (a) Bacterial internalization was measured in control and ELMO1 shRNA J774 cells challenged with Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium (SL1344), E. coli strain K12, and E. coli DH5α. (b) The percentage of bacterial internalization was compared between control and ELMO1 shRNA J774 cells, bacterial internalization for control cells was taken as 100% as performed in A. (c) The level of TNF-α was measured in control and ELMO1 shRNA J774 cells challenged with SL1344, E. coli K12, and E. coli DH5α after 3 h. Data in (a), (b), and (c) represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *, **, *** means p ≤ 0.05, ≤ 0.01, and ≤ 0.001, respectively, as assessed by unpaired two-tailed Student t-test. (d) BLAST-Protein search using the amino acid sequence of Shigella IpgB1 with all other bacteria identified sequence similarities with a signature motif (WxxxE or Trp-x-x-x-Glu) present in bacterial effectors from enteric pathogens but absent in commensals. (e) GST pulldown was performed with control GST and GST-SifA with the lysates from control and ELMO1 shRNA J774 cells. The input was shown on the left side and immunoblotted with anti-ELMO1 antibody. α -Tubulin was used as a loading control. (f) HEK 293 cells were transfected with either the vector control or with the EGFP-SifA (with WxxxE signature motif)+FLAG-ELMO1 or with the EGFP-SifAE201A (WxxxE mutant motif)+FLAG-ELMO1. The lysates from each condition were used either as input (left) or used for EGFP pulldown, followed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG antibody to know the level of FLAG-ELMO1. Equal loading is confirmed by the EGFP antibody (lower panel). (g) GST pulldown with either the GST alone or with GST-ELMO1 was incubated with His-SifA WT (with WxxxE signature motif) and His-SifA E201A (WxxxE mutant motif). The pulldown samples were immunoblotted with anti-His antibody (upper panel). The equal loading of beads is confirmed by anti-GST antibody (lower panel)
