Figure 2.
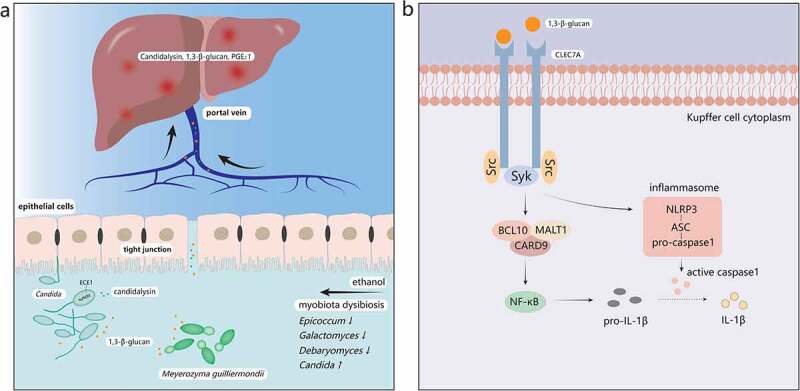
The mechanisms of ALD induced by the gut mycobiota. a. Ethanol abuse leads to disordered gut mycobiota. Epicoccum, Galactomyces, and Debaryomyces decrease, while Candida increases significantly in the intestine. 1,3-β-glucan, a main component of fungal cell walls, and Candidalysin, a fungal metabolite, translocate into the systemic circulation through the injured intestinal barrier and reach the liver first. b. 1,3-β-glucan binds to dectin-1 of Kupffer cells. Src kinases phosphorylate tyrosine residue of dectin-1 and recruit Syk, which can activate the CARD9/BCL10/MALT1 complex. Then NF-κB will be activated by the complex and produce pro-IL-1β. Syk also promotes the secretion of caspase-1 through the activated NLRP3/ASC/pro-caspase-1 complex. Caspase-1 then cleaves pro-IL-1β into mature IL-1β, mediating liver inflammation and damage. Syk, spleen tyrosine kinase; CARD9, caspase recruitment domain 9; BCL10, B-cell lymphoma 10; MALT1, mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma-translocation gene 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD
