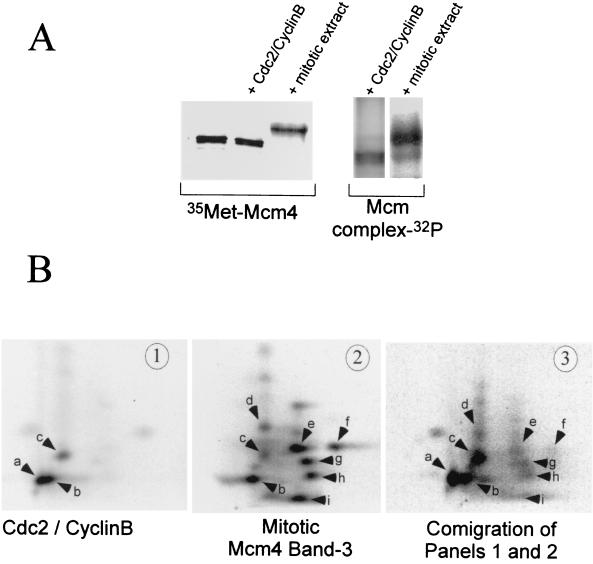
FIG. 3.
Mitotic hyperphosphorylation of the Mcm4 protein requires Cdc2-cyclin B and other kinases. (A) In vitro phosphorylation of Mcm4 by purified Cdc2-cyclin B or a mitotic extract. Phosphorylation reactions were run in kinases buffer containing either 50 U of purified Cdc2-cyclin B or 10 μl of mitotic extract. The substrate was 4 μl of an in vitro-translated [35S]methionine labeled Mcm4 protein or Mcm4 present in an interphase Mcm complex. After a 1-h incubation at room temperature the Mcm proteins were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Mcm4 antibody and separated by SDS-PAGE. The mobility shift of the Mcm4 protein was detected by visualizing both the [35S]methionine label and the incorporated 32P by using a PhosphorImager. The mobility shift of the Mcm4 protein was also confirmed by Western blot analyses (data not shown). (B) Two-dimensional tryptic phosphopeptide mapping was performed on the Mcm4 protein phosphorylated in vitro by Cdc2-cyclin B (panel 1) or in a mitotic extract (panel 2). In panel 3 the two-dimensional phosphopeptide map of a mixture containing samples 1 and 2 is shown. Electrophoretic separation was performed along the horizontal axis, and ascending chromatography was done along the vertical axis.