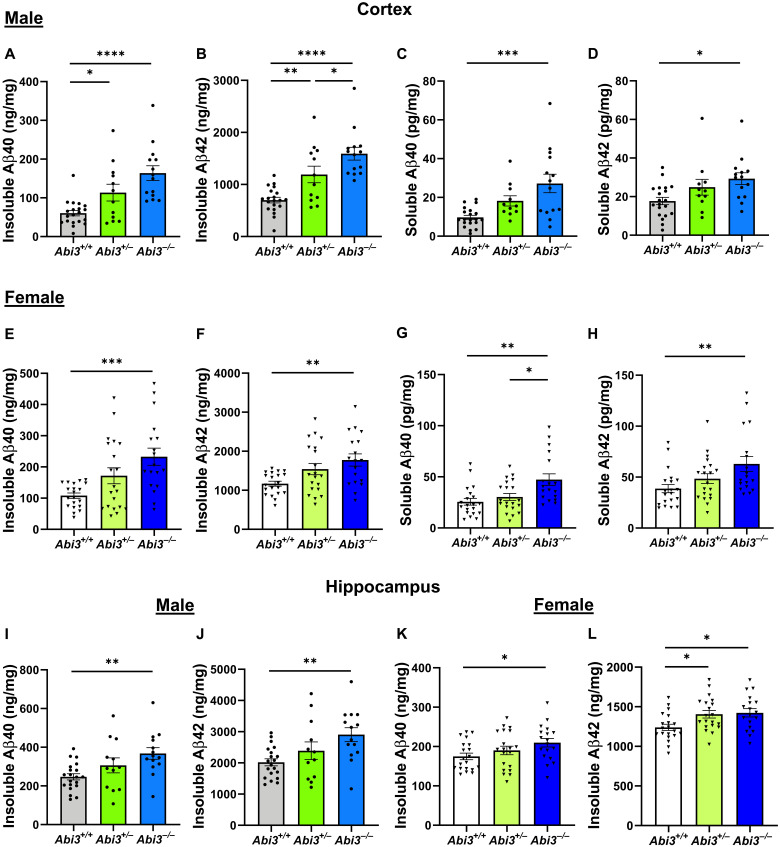
Fig. 1. Aβ accumulation increases in the cortex and hippocampus of male and female Abi3−/− mice.
Insoluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels were measured in the guanidine fraction (A and B) and soluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels were measured in the phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) fraction (C and D) of 5XFAD mouse cortices using Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) electrochemiluminescence assay. Insoluble Aβ40 (A) and Aβ42 (B) levels were increased in the cortices of 8-month-old male Abi3+/− and Abi3−/− mice compared to Abi3+/+ mice. Soluble Aβ40 (C) and Aβ42 (D) levels were increased in the cortices of 8-month-old male Abi3−/− mice compared to Abi3+/+ mice. Insoluble Aβ40 (E) and Aβ42 (F) levels were increased in the cortices of 8-month-old female Abi3−/− mice compared to Abi3+/+ mice. Soluble Aβ40 (G) and Aβ42 (H) levels were increased in the cortices of 8-month-old female Abi3−/− mice compared to Abi3+/+ mice. (I to L) Insoluble Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels were measured in the hippocampus. Male Abi3−/− mice accumulated higher levels of (I) Aβ40 and (J) Aβ42. Similarly, female Abi3−/− mice had higher levels of (K) Aβ40 and (L) Aβ42 (Abi3+/+, n = 20 male and 20 female; Abi3+/−, n = 12 male and 20 female; Abi3−/−, n = 14 male and 18 female). Data represent means ± SEM. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. See also fig. S3.