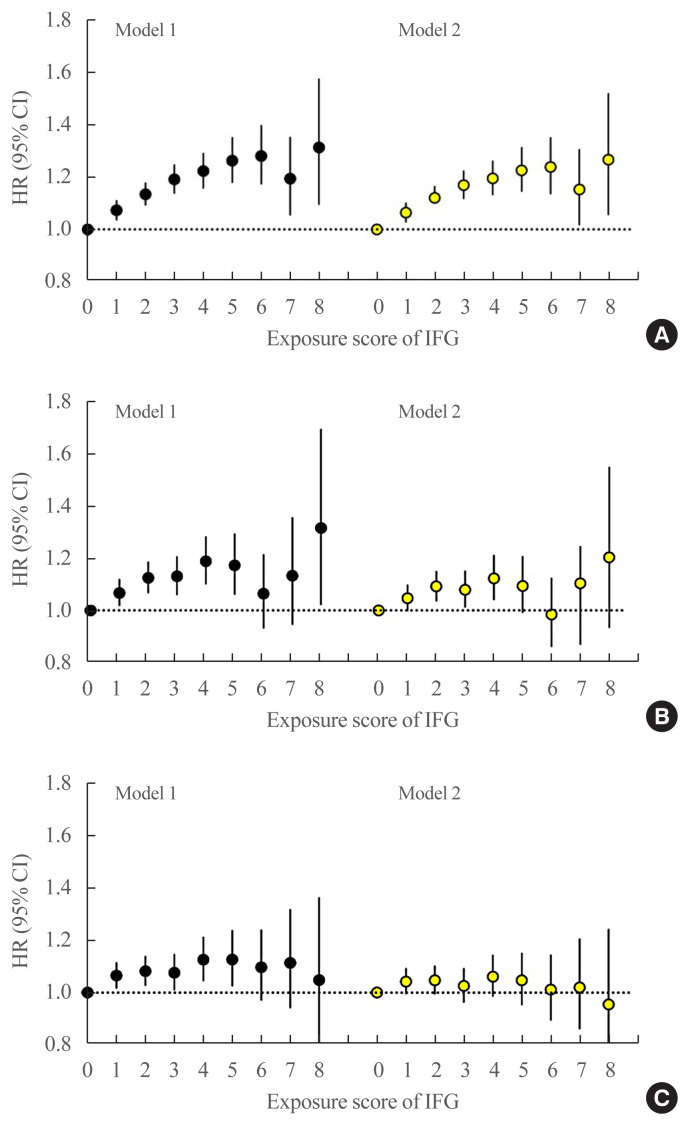
Fig. 3.
Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for (A) all-cause mortality, (B) myocardial infarction, and (C) stroke according to the severity-weighted impaired fasting glucose (IFG) exposure score ranging from 0 to 8. This IFG score was defined by assigning 0, 1, and 2 points to FBG levels of <100, 100–109, and 110–125 mg/dL, respectively. These scores were then summed to generate an IFG exposure score ranging from 0 to 8 points. A person with a score of 8 points corresponds to a person with a FBG ≥110 mg/dL at all annual health checkups over 4 years. The left-hand panel shows data adjusted for age, sex, alcohol consumption, smoking, physical activity, and body mass index (model 1). The right-hand panel presents data upon full adjustment for covariates including hypertension and dyslipidemia (model 2).