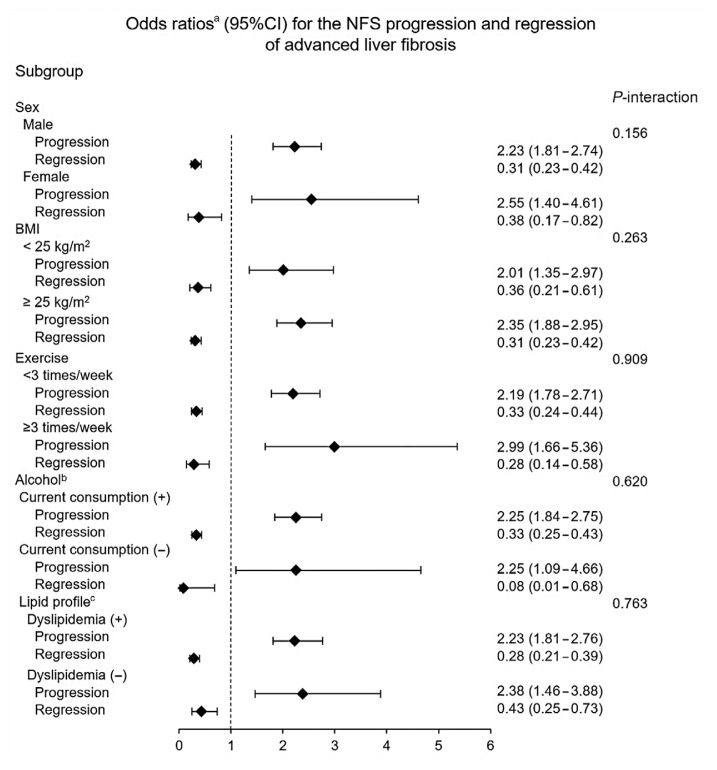
Fig. 3.
Odds ratio for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) fibrosis score (NFS)-based fibrosis progression and regression in participants belonging to G4 (group with highest increase in homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance [HOMA-IR]) compared to G1 (group with decreased HOMA-IR). CI, confidence interval; BMI, body mass index. aAdjusted for sex, center (Seoul or Suwon), systolic blood pressure, regular exercise, current alcohol consumption, smoking status, waist circumference, hemoglobin A1c, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglycerides, new onset diabetes, and baseline HOMA-IR; bCurrent alcohol consumption was defined as daily alcohol consumption above the median value (12 g/day for men and 2 g/day for women); cDyslipidemia was defined as an LDL-C level >3.4 mmol/L, total cholesterol level >5.2 mmol/L, triglyceride >1.7 mmol/L, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol <0.9 mmol/L for men and <1.3 mmol/L for women, or the current use of anti-dyslipidemia medication.