Figure 1.
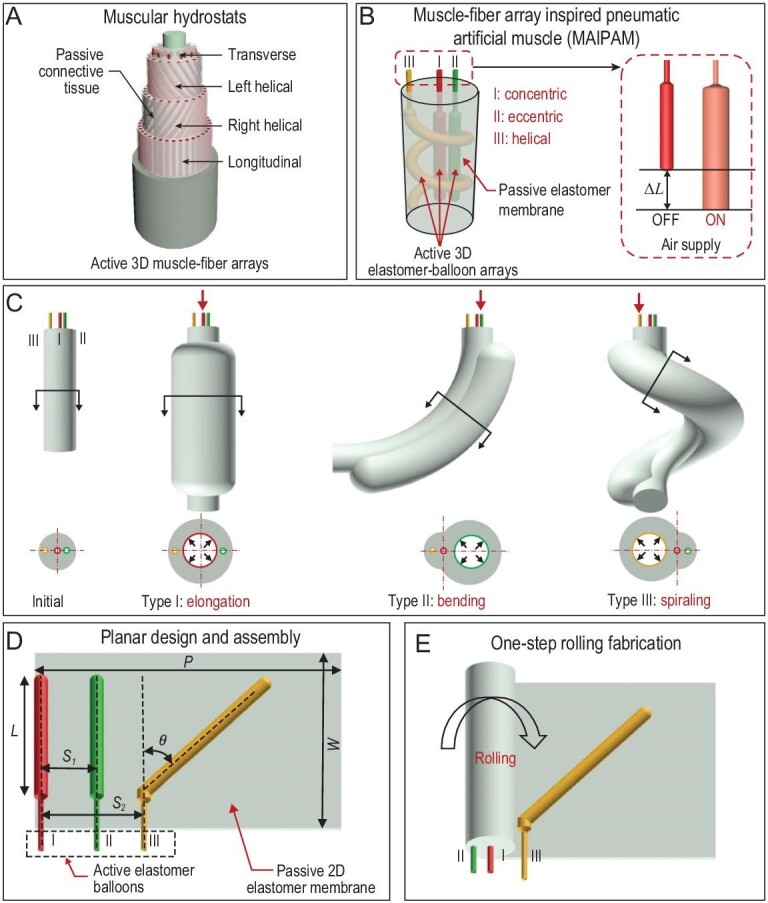
Design and fabrication principle of the MAIPAMs. (A) Schematic of the skeleton-free muscular hydrostats. Muscular hydrostats mainly consist of active three-dimensional (3D) muscle-fiber arrays (including transverse, left-helical, right-helical and longitudinal muscle fibers) reinforced by passive connective tissues, enabling multiple-mode actuations and versatile manipulation by selectively actuating the muscle-fiber arrays. (B) The morphology of the designed MAIPAMs, consisting of active 3D elastomer-balloon arrays (cylinder latex elastomer balloon with an outer diameter of 5 mm and a wall thickness of 0.3 mm) reinforced by a passive 2D elastomer membrane (3M VHB 4910 with inherent strong adhesive, a thickness of 1 mm). The arrays contain three kinds of active elastomer balloons: concentric (type I), eccentric (type II) and helical (type III) active elastomer balloons. (C) Multiple-mode actuations of the MAIPAMs. Upon a supplied pressure, the elongation of active elastomer balloons can be converted into elongation (type I balloon), bending (type II balloon) and spiraling (type III balloon), respectively. (D) Schematic of the planar design and assembly of the MAIPAMs (Fig. S2 and Movie S1): (i) determine the design parameters of active elastomer balloons (including the length L of the active elastomer balloon, the distance S between the active elastomer balloon and the edge of the passive elastomer membrane, and the oblique angle 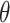 ); (ii) assemble the active elastomer balloons in a passive 2D elastomer membrane. (E) Working principle of the one-step fabrication approach for rolling the passive 2D elastomer membrane into a 3D MAIPAM (Movie S1).
); (ii) assemble the active elastomer balloons in a passive 2D elastomer membrane. (E) Working principle of the one-step fabrication approach for rolling the passive 2D elastomer membrane into a 3D MAIPAM (Movie S1).
