Figure 2.
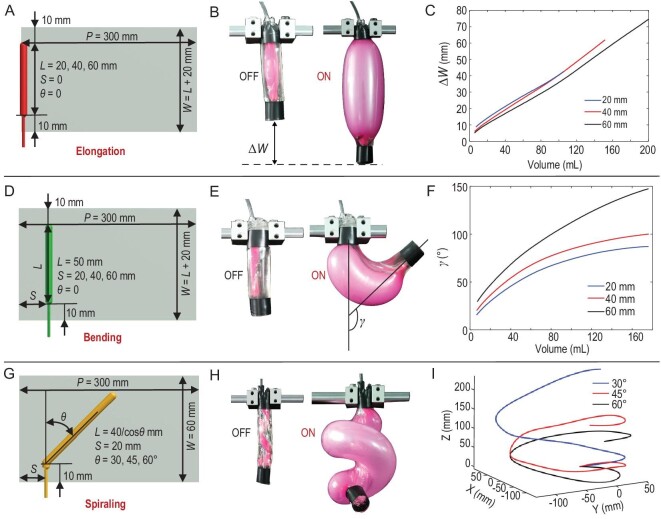
Characterization of the design parameters on the actuation modes of the MAIPAMs. (A) Schematic of the 2D-based design pattern of the elongated MAIPAMs. An active elastomer balloon (type I) is assembled at position (L > 0, S = 0, 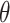 = 0) in the passive 2D elastomer membrane. (B) The working principle of the elongated MAIPAMs: upon supplied volume V of the compressed air, the MAIPAMs generate an elongated displacement
= 0) in the passive 2D elastomer membrane. (B) The working principle of the elongated MAIPAMs: upon supplied volume V of the compressed air, the MAIPAMs generate an elongated displacement 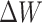 . (C)
. (C) 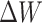 is plotted as a function of V when L equals 20, 40 and 60 mm, respectively. (D) Schematic of the 2D-based design pattern of the bending MAIPAMs. An active elastomer balloon (type II) is assembled at position (L = 50 mm, S > 0,
is plotted as a function of V when L equals 20, 40 and 60 mm, respectively. (D) Schematic of the 2D-based design pattern of the bending MAIPAMs. An active elastomer balloon (type II) is assembled at position (L = 50 mm, S > 0, 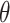 = 0) in the passive 2D elastomer membrane. (E) The working principle of the bending MAIPAMs: upon supplied volume V of the compressed air, the MAIPAMs generate a bending angle
= 0) in the passive 2D elastomer membrane. (E) The working principle of the bending MAIPAMs: upon supplied volume V of the compressed air, the MAIPAMs generate a bending angle 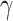 . (F)
. (F) 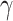 is plotted as a function of V when S equals
20, 40 and 60 mm, respectively. (G) Schematic of the 2D-based design pattern of the spiraling MAIPAMs. An active elastomer balloon (type III) is assembled at position (L = 40/cos
is plotted as a function of V when S equals
20, 40 and 60 mm, respectively. (G) Schematic of the 2D-based design pattern of the spiraling MAIPAMs. An active elastomer balloon (type III) is assembled at position (L = 40/cos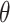 mm, S = 20 mm,
mm, S = 20 mm, 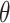 >0) in the passive 2D elastomer membrane. (H) The working principle of the spiraling MAIPAMs: upon supplied volume V of the compressed air, they form helical shapes. (I) The helical shapes of the spiraling MAIPAMs with different
>0) in the passive 2D elastomer membrane. (H) The working principle of the spiraling MAIPAMs: upon supplied volume V of the compressed air, they form helical shapes. (I) The helical shapes of the spiraling MAIPAMs with different 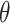 when V equals 120 mL with a pressure of 46.5 kPa.
when V equals 120 mL with a pressure of 46.5 kPa.