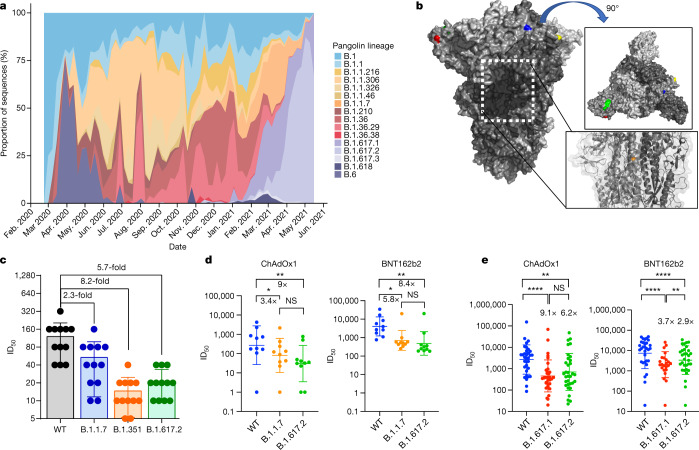
Fig. 1. Rapid expansion of Delta variant B.1.617.2 cases in India and reduced sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies from sera derived following infection and vaccination.
a, Proportion of lineages in incident cases of SARS-CoV-2 in India 2020–2021. b, Surface representation of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.671.2 spike trimer (PDB: 6ZGE). Red, L19R; green, del157/158; blue, L452R; yellow, T478K. The white dotted box indicates the location of the D950N substitution (orange). c, Neutralization of the Delta variant by convalescent human serum from mid-2020. Fold change in serum neutralization of 100 TCID50 of B.1.17 (Alpha), B.1.351 (Beta) and B.1617.2 (Delta) variants relative to WT (IC19); n = 12. Shown is the ID50, the serum dilution required for 50% virus inhibition, expressed as GMT (from technical replicates) with s.d. d, Neutralization of B.1617.2 live virus by sera from vaccinated individuals (n = 10 ChAdOx1 or n = 10 BNT12b2), compared with B.1.1.7 and Wuhan-1 WT. The graph presents the average of two independent experiments. e, Neutralization of B.1.617 spike PV and WT (Wuhan-1 D614G) by vaccine sera (n = 33 ChAdOx1 or n = 32 BNT162b2). The data are representative of two independent experiments each with two technical replicates. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001 (Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test); NS, not significant.