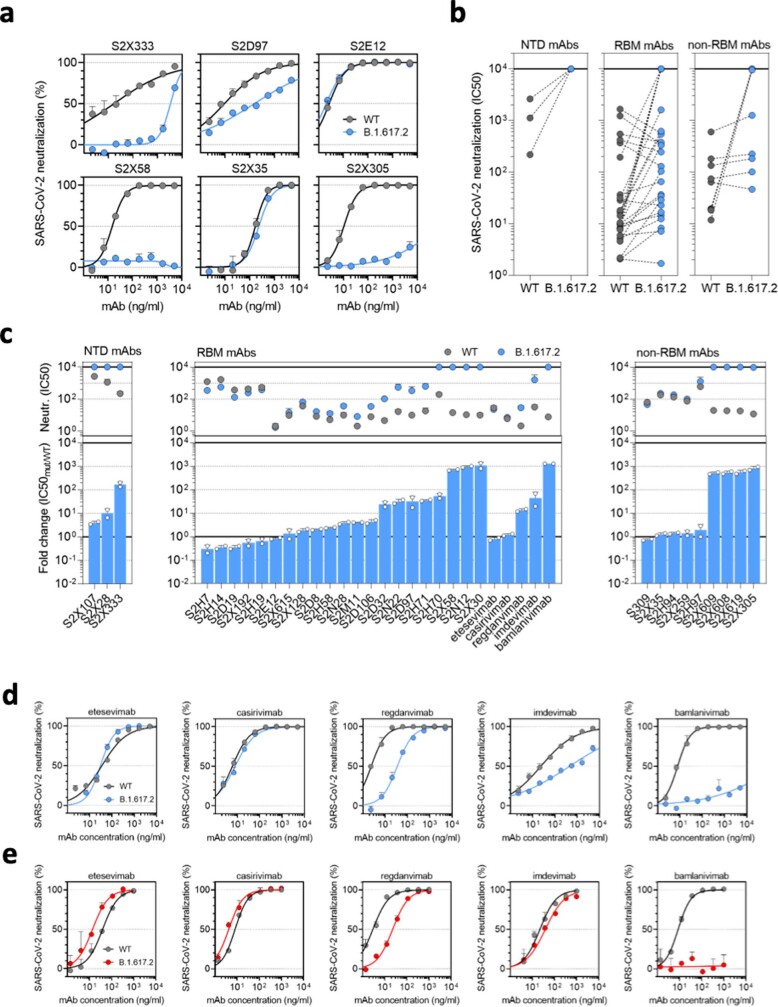
Extended Data Fig. 1. Delta variant B.1.617.2 shows reduced sensitivity to monoclonal antibodies.
Neutralisation by a panel of NTD- and RBD-specific mAbs against WT and B.1.617.2 mutant SARS-CoV-2 pseudotyped viruses. a. Neutralisation of WT D614 (black) and B.1.617.2 mutant (blue) pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2-VSV by 6 selected mAbs from one representative experiment out of 2 independent experiments. S2X333 is an NTD-specific mAb, S2D97, S2E12 and S2X58 are RBM-specific mAbs, while S2X35 and S2X305 are non-RBM mAbs. b. Neutralisation of WT and B.1.617.2 VSV by 38 mAbs targeting NTD (n = 3), RBM (n = 26, including 5 clinical stage mAb) and non-RBM (n = 9). Shown are the mean IC50 values (ng/ml) from 2 independent experiments. Non-neutralising IC50 titers were set at 104 ng/ml. c. Neutralisation shown as mean IC50 values (upper panel) and average fold change of B.1.617.2 relative to WT (lower panel) of 38 mAbs tested in 2 independent experiments (including 5 clinical-stage mAbs), tested using Vero E6 cells expressing TMPRSS2. d–e, Neutralisation of WT D614 (black) and B.1.617.2 mutant (blue/red) pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2-VSV by 5 clinical-stage mAbs using Vero E6 cells expressing TMPRSS2 (d) or not (e). Shown is one representative experiment out of 2 independent experiments.