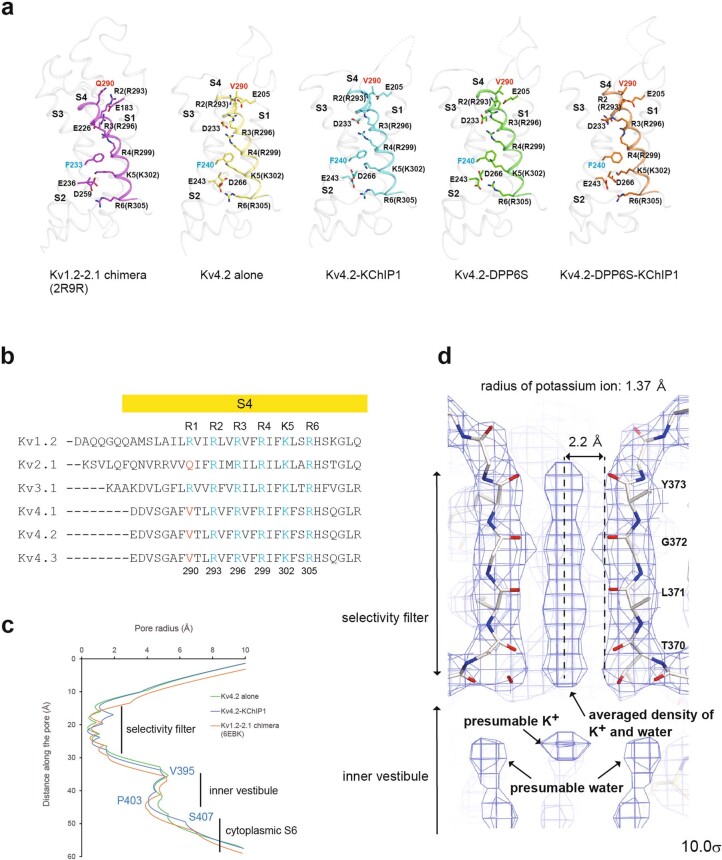
Extended Data Fig. 6. Kv4.2 adopts the S4 up and S6 open conformation.
a. Structures of the voltage sensors (S1-S4) from Kv1.2-2.1, Kv4.2 alone, Kv4.2–KChIP1, Kv4.2–DPP6S, and Kv4.2–DPP6S–KChIP1. S4 helices are coloured. Arg/Lys gating charges as well as other key residues are shown with side chains. The positions of positively charged amino acid residues in the S4 helix relative to a phenylalanine residue in the S2 helix indicates that the present S4 helix of Kv4.2 adopts the depolarized “up” conformation in all of four structures. b. Alignment of S4 amino acid sequences among the closely related Kv1 to Kv4. c. Radii of the pores of Kv4.2 alone, Kv4.2–KchIP1, and the Kv1.2-2.1 chimera, calculated using the HOLE program. d. The density map of the Kv4.2–KChIP1 complex at the selectivity filter shows the averaged densities of potassium ions and water. The S6 helix forming the pore adopts an open conformation, with the selectivity filter occupied by dehydrated K+ ions and water molecules, through the close interaction with the S4-S5 linker, as observed in the Kv1.2 structure30 (Extended Data Figs. 5a, b). The previous electrophysiological studies reported that upon depolarization, Kv4s adopt the closed conformation (i.e. CSI) at all physiologically relevant membrane potentials within a cell11–18 (Extended Data Fig. 1). This discrepancy could be attributed to the micelle which is likely to facilitate the open conformation. Similar inconsistent example was observed in the cryo-EM structure of the HCN channel in a hyperpolarized conformation in which the pore is closed while it is open within a cell57.