Extended Data Fig. 14. Model for Kv4 modulation by KChIP and DPP.
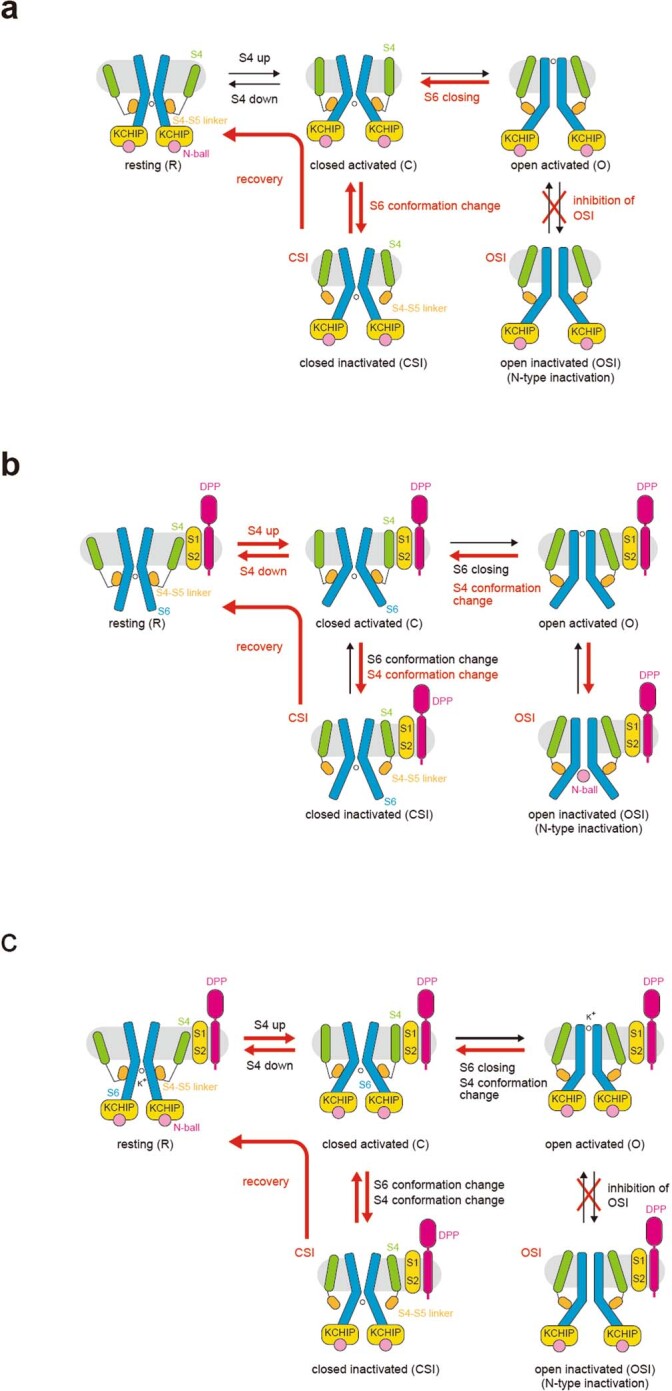
a. Model for Kv4 modulation by KChIP. KChIPs capture the Kv4 N- and C-termini, thereby inhibiting open state inactivation (OSI). On the other hand, KChIPs stabilize the S6 conformation and might enable synchronized movement of the four S6 gating helices, thereby accelerating closed state inactivation and recovery. b. Model for Kv4 modulation by DPP. DPPs might stabilize the conformation of Kv4 S1-S2 and facilitate S4 conformational change, including S4 sliding up and down, thereby accelerating activation, inactivation, and recovery. c. Model for Kv4 modulation in the Kv4–DPP–KChIP ternary complex. KChIPs capture the Kv4 N- and C-termini of two adjacent subunits, thereby prevent open state inactivation (OSI). As a result, Kv4 ternary complex preferentially inactivates from a closed activated state (CSI). In addition, KChIPs stabilize the S6 conformation and accelerates S6 gating. DPPs stabilize the conformation of Kv4 S1-S2 and accelerates S4 conformation change including S4 movement upon membrane voltage shift. All together additive modulations by KChIPs and DPPs confer A-type current characterized as fast activation, fast closed state inactivation, and fast recovery.
